Temporal Bone Fracture
Benjamin Y. Huang
CLINICAL HISTORY
26-year-old male involved in a rollover motor vehicle collision, now with right-sided hearing loss and facial paralysis.
FINDINGS
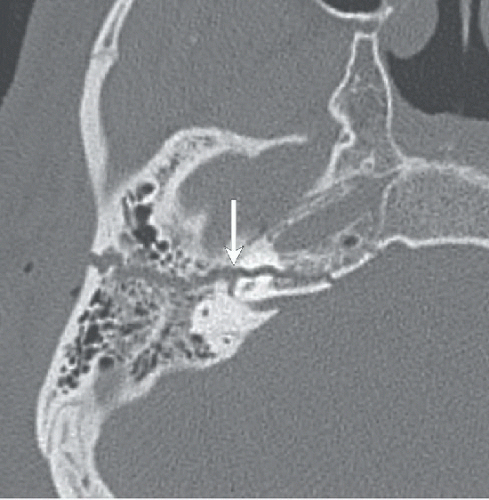
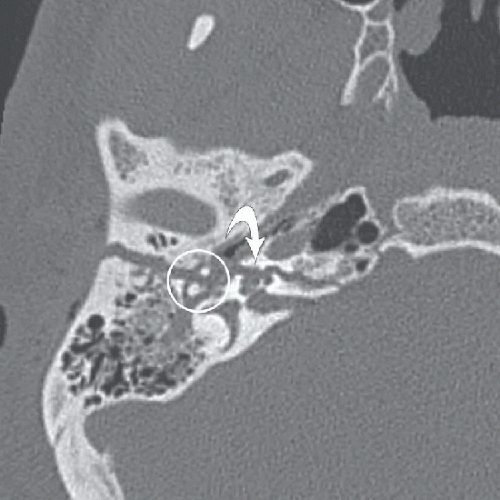
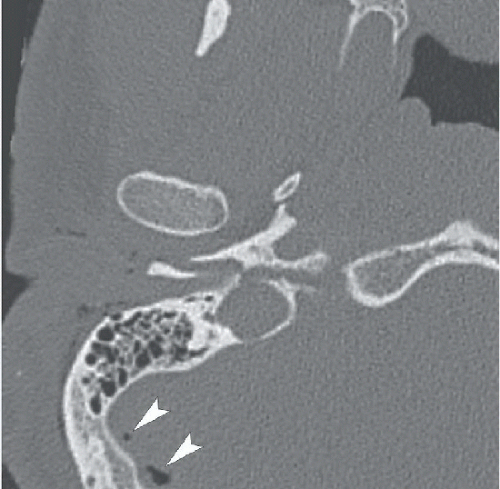
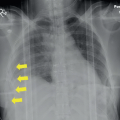
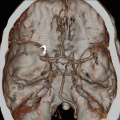
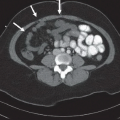
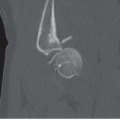
Figures 73A,73B and 73C: Axial unenhanced CT through the right temporal bone demonstrate an obliquely oriented fracture coursing from the lateral mastoid cortex through the petrous apex. The fracture line extends through the fossa for the geniculate ganglion of the facial nerve (arrow in Fig. 73A) and through the cochlea (curved arrow in Fig. 73B). There is widening of the malleoincudal joint indicating joint dislocation (circled area in Fig. 73B). In Figure 73C, the fracture can be seen to extend through the anterior wall of the external auditory canal and between the carotid canal and jugular foramen. There is also pneumocephalus in the posterior fossa (arrowheads), indicating the presence of a CSF fistula.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree