Chapter 6 Transducers
INTRODUCTION
The transducer is one of the most critical components of any diagnostic ultrasound system. There are many types of ultrasound transducers that can be selected before performing an ultrasound investigation as seen in Figure 6.1, and a great deal of attention should be paid to selecting the most appropriate transducer for the application.
We need to be aware that there is a trade-off between image resolution and the penetrating depth of ultrasound which is governed by its frequency. For example, a 12 MHz transducer has very good resolution, but cannot penetrate very deep into the body compared to a 3 MHz transducer which can penetrate deep into the body, but the resolution is not as good as the transducer operating at 12 MHz. In general use, the highest frequency transducer which will reach the required depth should always be employed.
THE TRANSDUCER
Components and Construction of a Typical Transducer
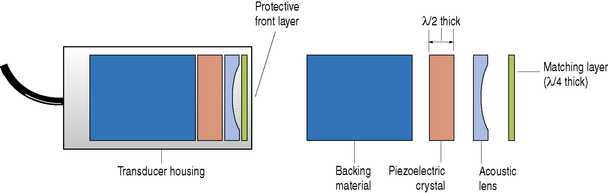
There are many types of transducers ranging from a simple single element to electronic multi-array probes which have hundreds of elements. The components and construction of these different types of transducers are principally the same. To understand how modern day electronic multi-element transducers function we need to start by considering the construction and components of a simple single element circular transducer. This is illustrated in Figure 6.2.
The main components of a typical ultrasound transducer consist of:
Electrical connections
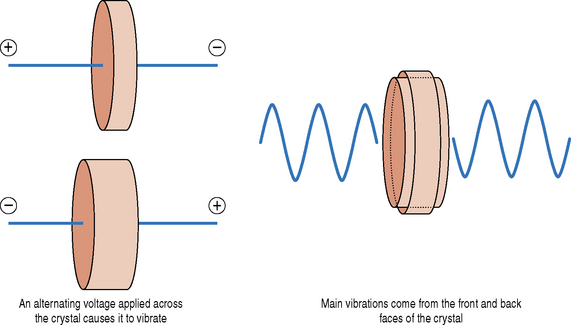
Two electrical connections are formed on the front and back face of the crystal by plating a thin film of gold or silver on these surfaces. These electrodes are connected to the ultrasound machine which generates the short burst of electrical pulses to excite the crystal and through the piezoelectric effect generates a pulse of ultrasound energy.
Piezoelectric element
Purpose of the backing material
Let us consider a simple single element transducer as illustrated in Figure 6.3. When a short burst or pulse of electricity is applied to a crystal it causes it to vibrate in all directions. The main vibrations come from the front and back faces of the piezoelectric crystal. We are only interested in the vibrations that come off the front face of the transducer. To try and eliminate the vibrations from the back face, and to control the length of vibrations from the front face, a backing or damping material is used. This damping material, which typically consists of tungsten powder and plastic or epoxy resin, is attached to the back face of the piezoelectric crystal.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree