| SKULL BASE REGION | Trigeminal cistern |
| HISTOPATHOLOGY | N/A |
| PRIOR SURGICAL RESECTION | N/A |
| PERTINENT LABORATORY FINDINGS | N/A |
Case description
The patient is an 82-year-old woman who suffered from tic douloureux in the left V2 and V3 territory. Her pain was initially well controlled on carbamazepine, but progressively became highly resistant to polytherapy. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) demonstrated a major neurovascular conflict between the cisternal portion of the trigeminal nerve and a dolichoectatic basilar artery. Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) was recommended ( Figure 9.42.1 ), and the patient agreed to proceed with treatment.
| Radiosurgery Machine | Gamma Knife – Icon |
| Radiosurgery Dose (Gy) | 90 at the 100% isodose point |
| Number of Fractions | 1 |

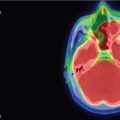
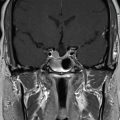
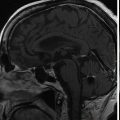
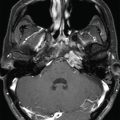
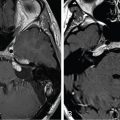
Imaging of the treatment plan. The dose planning is displayed in axial CISS images fused with computed tomography (CT) bony window ( A ), axial CT bony window ( B ), coronal CISS images fused with CT bony window ( C ), and sagittal CISS images ( D ). Following Leksell G frame application under local anesthesia, an MRI and a CT scan were performed for stereotactic purposes. The MRI included a high-resolution, 0.5 mm 3 T2 CISS sequence and a 3D T1 MPR sequence on a 1.5 T Siemens MR machine. A single 4-mm isocenter was positioned 7–8 mm anterior to the nerve emergence from the pons, on the cisternal portion of the left trigeminal nerve. A dose of 90 Gy was prescribed at the 100% isodose point. The treatment time was 53 minutes. CISS, Constructive interference in steady state; MPR, multiplanar reformation (reconstruction).
| Critical Structure | Dose Tolerance |
|---|---|
| Brainstem | < 0.01 cc > 15 Gy |
| Basilar artery | Very tolerant |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree