Chapter 19 Ultrasonography
Understanding the Principles and Recognizing Normal and Abnormal Findings
 Ultrasound (US) occupies an acoustical frequency on the electromagnetic spectrum that is hundreds of times greater than humans can hear. Ultrasonography is the medical imaging modality that utilizes that acoustical energy to localize and characterize human tissues.
Ultrasound (US) occupies an acoustical frequency on the electromagnetic spectrum that is hundreds of times greater than humans can hear. Ultrasonography is the medical imaging modality that utilizes that acoustical energy to localize and characterize human tissues.How it Works
 The creation of a sonographic image (sonogram) depends on three major components: the production of a high frequency sound wave, the reception of a reflected wave or echo, and the conversion of that echo into the actual image.
The creation of a sonographic image (sonogram) depends on three major components: the production of a high frequency sound wave, the reception of a reflected wave or echo, and the conversion of that echo into the actual image. The sound wave is produced by a probe that contains one of more transducers, which send out extremely short bursts of acoustical energy at a given frequency.
The sound wave is produced by a probe that contains one of more transducers, which send out extremely short bursts of acoustical energy at a given frequency. Like all sound waves, the pulses produced by the transducer travel at different speeds depending on the density of the medium through which they are traveling.
Like all sound waves, the pulses produced by the transducer travel at different speeds depending on the density of the medium through which they are traveling. Where the wave strikes an interface between tissues of differing densities, some of the sound will be transmitted forward while some will be reflected back to the transducer.
Where the wave strikes an interface between tissues of differing densities, some of the sound will be transmitted forward while some will be reflected back to the transducer. If the pulse encounters fluid, most of the acoustical energy is transmitted. If the pulse encounters gas or bone, so much of the acoustical energy is reflected back that it is usually not possible to define deeper structures.
If the pulse encounters fluid, most of the acoustical energy is transmitted. If the pulse encounters gas or bone, so much of the acoustical energy is reflected back that it is usually not possible to define deeper structures. When the echo arrives back at the transducer (a matter of microseconds), it is converted from sound into electrical pulses that are then sent to the scanner itself.
When the echo arrives back at the transducer (a matter of microseconds), it is converted from sound into electrical pulses that are then sent to the scanner itself. Using an on-board computer, the scanner determines the length of time it took for the echo to be received, the frequency of the reflected echo, and the magnitude or amplitude of the signal. With this information, a sonographic image of the scanned body part can be generated by the computer and recorded digitally, on film, or sometimes on videotape.
Using an on-board computer, the scanner determines the length of time it took for the echo to be received, the frequency of the reflected echo, and the magnitude or amplitude of the signal. With this information, a sonographic image of the scanned body part can be generated by the computer and recorded digitally, on film, or sometimes on videotape. A tissue that reflects many echoes is said to be echogenic (hyperechoic) and is usually depicted as bright or white on the sonogram; a tissue that has few or no echoes is said to be sonolucent (hypoechoic or anechoic) and is usually depicted as being dark or black.
A tissue that reflects many echoes is said to be echogenic (hyperechoic) and is usually depicted as bright or white on the sonogram; a tissue that has few or no echoes is said to be sonolucent (hypoechoic or anechoic) and is usually depicted as being dark or black. Also by convention, sonographic images are viewed with the patient’s head to your left and the patient’s feet toward your right; anterior is up and posterior is down.
Also by convention, sonographic images are viewed with the patient’s head to your left and the patient’s feet toward your right; anterior is up and posterior is down.TABLE 19-1 TYPES OF ULTRASOUND
| A-Mode | Simplest; spikes along a line represent the signal amplitude at a certain depth; used mainly in ophthalmology. |
| B-Mode | Mode most often used in diagnostic imaging; each echo is depicted as a dot and the sonogram is made up of thousands of these dots; can depict real-time motion. |
| M-Mode | Used to show moving structures such as blood flow or motion of the heart valves. |
| Doppler | Uses the Doppler effect to assess blood flow; used for vascular ultrasound. Pulsed Doppler devices emit short bursts of energy that allow for an accurate localization of the echo source and has replaced continuous wave Doppler. |
| Duplex ultrasonography | Utilized in vascular studies; refers to the simultaneous use of both gray-scale or color Doppler to visualize the structure of and flow within a vessel and spectral waveform Doppler to quantitate flow. |
Doppler Ultrasonography
 You are probably familiar with the common examples of a passing train whistle or police siren as illustrations of the Doppler effect, which generally states that sound changes in frequency as the object producing the sound approaches or recedes from your ear.
You are probably familiar with the common examples of a passing train whistle or police siren as illustrations of the Doppler effect, which generally states that sound changes in frequency as the object producing the sound approaches or recedes from your ear. Sonography makes use of the Doppler effect to determine if an object, usually blood, is moving toward or away from the transducer and at what velocity it is moving.
Sonography makes use of the Doppler effect to determine if an object, usually blood, is moving toward or away from the transducer and at what velocity it is moving.Adverse Effects and Safety Issues
 The procedure is well tolerated. Scans can be obtained quickly, done at the bedside if necessary, and, for the most part, require no patient preparation other than eating no food before abdominal studies (Table 19-2).
The procedure is well tolerated. Scans can be obtained quickly, done at the bedside if necessary, and, for the most part, require no patient preparation other than eating no food before abdominal studies (Table 19-2). Ultrasound has the short-term potential to cause minor elevation of heat in the area being scanned, though not at levels used in diagnosis.
Ultrasound has the short-term potential to cause minor elevation of heat in the area being scanned, though not at levels used in diagnosis.TABLE 19-2 ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF ULTRASONOGRAPHY
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| No ionizing radiation No known long-term side effects “Real-time” images Produces little or no patient discomfort Small, portable, inexpensive, ubiquitous | Difficulty penetrating through bone Gas-filled structures reduce its utility Obese patients may be difficult to penetrate Dependent on the skills of the operator scanning |
Medical Uses of Ultrasonography
 Ultrasound is widely used in medical imaging. It is usually the study of first choice in imaging the female pelvis and in pediatric patients, in differentiating cystic versus solid lesions in all patients, in noninvasive vascular imaging, imaging of the fetus and placenta during pregnancy, and in real-time, image-guided fluid aspiration and biopsies.
Ultrasound is widely used in medical imaging. It is usually the study of first choice in imaging the female pelvis and in pediatric patients, in differentiating cystic versus solid lesions in all patients, in noninvasive vascular imaging, imaging of the fetus and placenta during pregnancy, and in real-time, image-guided fluid aspiration and biopsies. Other common uses are evaluation of cystic versus solid breast masses, thyroid nodules, tendons, and in assessing the brain, hips, and spine in newborns. Ultrasound is used everywhere from intraoperative scanning in the surgical suite to the medical unit in the battlefield and in locations as remote as the South Pole.
Other common uses are evaluation of cystic versus solid breast masses, thyroid nodules, tendons, and in assessing the brain, hips, and spine in newborns. Ultrasound is used everywhere from intraoperative scanning in the surgical suite to the medical unit in the battlefield and in locations as remote as the South Pole.Biliary System
 Ultrasound is the study of first choice for abnormalities of the biliary system. Patients who present with the relatively common complaint of right upper quadrant pain usually undergo an ultrasound examination first. CT may be helpful in cases with difficult or unusual anatomy, for detecting masses, or in determining the extent of disease already diagnosed, but CT is less sensitive than ultrasound in detecting gallstones.
Ultrasound is the study of first choice for abnormalities of the biliary system. Patients who present with the relatively common complaint of right upper quadrant pain usually undergo an ultrasound examination first. CT may be helpful in cases with difficult or unusual anatomy, for detecting masses, or in determining the extent of disease already diagnosed, but CT is less sensitive than ultrasound in detecting gallstones.Normal Ultrasound Anatomy
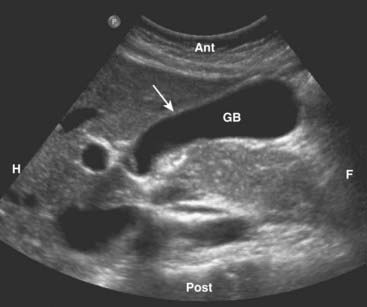
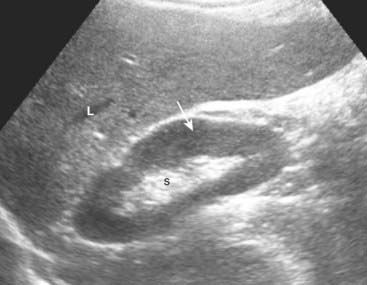
 The gallbladder is an elliptical sac that lies inferior and medial to the right lobe of the liver. Although different layers of its wall have different echogenic properties, the gallbladder overall consists of a fluid-filled sonolucent lumen surrounded by an echogenic wall. In the fasting patient, the gallbladder is about 4 × 10 cm in size and the wall is normally no thicker than 3 mm (Fig. 19-1).
The gallbladder is an elliptical sac that lies inferior and medial to the right lobe of the liver. Although different layers of its wall have different echogenic properties, the gallbladder overall consists of a fluid-filled sonolucent lumen surrounded by an echogenic wall. In the fasting patient, the gallbladder is about 4 × 10 cm in size and the wall is normally no thicker than 3 mm (Fig. 19-1).Gallstones and Acute Cholecystitis
 Cholelithiasis is estimated to affect more than 20 million Americans. In almost all cases, acute cholecystitis starts with a gallstone impacted in the neck of the gallbladder or cystic duct. The presence of gallstones does not, by itself, mean that the patient’s pain is from the gallbladder because asymptomatic gallstones are common. Cholecystitis can also occur less commonly in the absence of stones (acalculous cholecystitis).
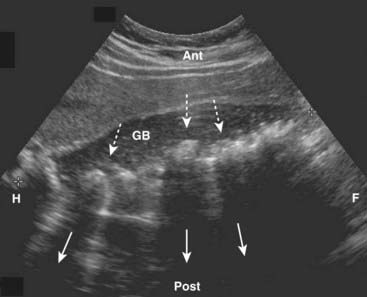
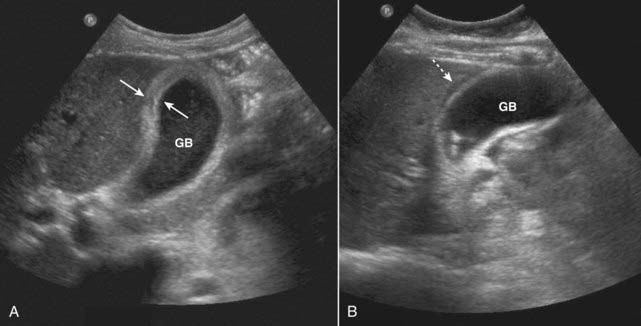
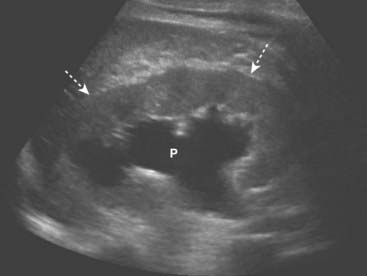
Cholelithiasis is estimated to affect more than 20 million Americans. In almost all cases, acute cholecystitis starts with a gallstone impacted in the neck of the gallbladder or cystic duct. The presence of gallstones does not, by itself, mean that the patient’s pain is from the gallbladder because asymptomatic gallstones are common. Cholecystitis can also occur less commonly in the absence of stones (acalculous cholecystitis). Gallstones usually fall to the most dependent part of gallbladder, which will depend on the patient’s position at the time of the scan. This helps to differentiate gallstones from polyps or tumors, which may be attached to a nondependent surface. Gallstones are characteristically echogenic and produce acoustical shadowing because they reflect most of the signal (Fig. 19-2).
Gallstones usually fall to the most dependent part of gallbladder, which will depend on the patient’s position at the time of the scan. This helps to differentiate gallstones from polyps or tumors, which may be attached to a nondependent surface. Gallstones are characteristically echogenic and produce acoustical shadowing because they reflect most of the signal (Fig. 19-2).![]() Acoustical shadowing describes a band of reduced echoes behind an echo-dense object (e.g., a gallstone) that reflects most, but not all, of the sound waves. While acoustical shadowing reduces the diagnostic effectiveness of ultrasound through such tissues as bone and bowel gas, its presence can have diagnostic value in identifying the presence of calculi, such as in the gallbladder and kidney (Fig. 19-3).
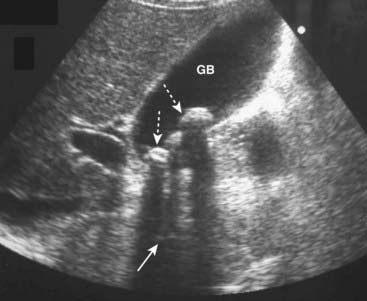
Acoustical shadowing describes a band of reduced echoes behind an echo-dense object (e.g., a gallstone) that reflects most, but not all, of the sound waves. While acoustical shadowing reduces the diagnostic effectiveness of ultrasound through such tissues as bone and bowel gas, its presence can have diagnostic value in identifying the presence of calculi, such as in the gallbladder and kidney (Fig. 19-3).
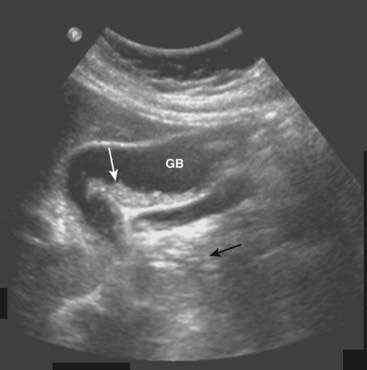
![]() Biliary sludge can be found in the lumen of the gallbladder and is an aggregation that may contain cholesterol crystals, bilirubin, and glycoproteins. It is often associated with biliary stasis. While it may be echogenic, sludge does not produce acoustical shadowing like gallstones (Fig. 19-4).
Biliary sludge can be found in the lumen of the gallbladder and is an aggregation that may contain cholesterol crystals, bilirubin, and glycoproteins. It is often associated with biliary stasis. While it may be echogenic, sludge does not produce acoustical shadowing like gallstones (Fig. 19-4).
 In the presence of gallstones and gallbladder wall thickening, ultrasound has a positive predictive value for acute cholecystitis as high as 94%.
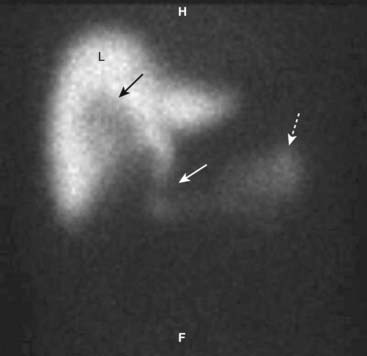
In the presence of gallstones and gallbladder wall thickening, ultrasound has a positive predictive value for acute cholecystitis as high as 94%. Radionuclide scans (HIDA scans) are also used in the diagnosis of acute cholecystitis.
Radionuclide scans (HIDA scans) are also used in the diagnosis of acute cholecystitis.Bile Ducts
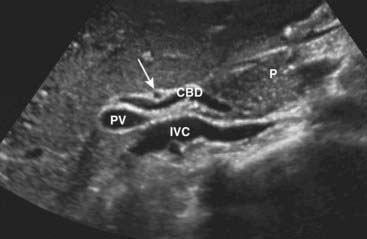
 Ultrasound plays a key role in evaluation of the intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts and pancreatic duct. The intrahepatic biliary radicals drain into the left and right hepatic ducts, which join to form the common hepatic duct (CHD). Where the cystic duct from the gallbladder joins the CHD is the origin of the common bile duct (CBD), which drains either within or adjacent to the head of the pancreas via the ampulla of Vater into the second portion of the duodenum. The CBD lies anterior to the portal vein and lateral to the hepatic artery in the porta hepatis (Fig. 19-7).
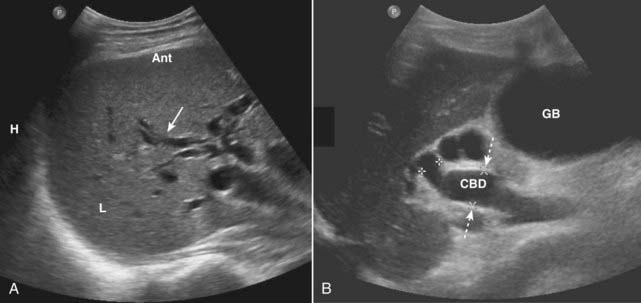
Ultrasound plays a key role in evaluation of the intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts and pancreatic duct. The intrahepatic biliary radicals drain into the left and right hepatic ducts, which join to form the common hepatic duct (CHD). Where the cystic duct from the gallbladder joins the CHD is the origin of the common bile duct (CBD), which drains either within or adjacent to the head of the pancreas via the ampulla of Vater into the second portion of the duodenum. The CBD lies anterior to the portal vein and lateral to the hepatic artery in the porta hepatis (Fig. 19-7). Normal intrahepatic bile ducts are not visible. When the CBD is obstructed, the extrahepatic ducts dilate before the intrahepatic ducts. Over time, both the intrahepatic and extrahepatic ducts will be dilated (Fig. 19-8).
Normal intrahepatic bile ducts are not visible. When the CBD is obstructed, the extrahepatic ducts dilate before the intrahepatic ducts. Over time, both the intrahepatic and extrahepatic ducts will be dilated (Fig. 19-8). Causes of bile duct obstruction include gallstones, pancreatic carcinoma, strictures, sclerosing cholangitis, cholangiocarcinoma, and metastatic disease.
Causes of bile duct obstruction include gallstones, pancreatic carcinoma, strictures, sclerosing cholangitis, cholangiocarcinoma, and metastatic disease.Urinary Tract
Normal Ultrasound Anatomy
 The kidneys normally measure 9-12 cm in length, 4-5 cm in width, and are 3-4 cm thick. The renal sinus is home to the renal pelvis and the major branches of the renal artery and vein. Because the renal sinus contains fat, it normally appears brightly echogenic. The calyces are normally not visible. The medullary pyramids are hypoechoic. The renal parenchyma has uniformly low echogenicity, which is usually less than that of the adjacent liver and spleen (Fig. 19-9).
The kidneys normally measure 9-12 cm in length, 4-5 cm in width, and are 3-4 cm thick. The renal sinus is home to the renal pelvis and the major branches of the renal artery and vein. Because the renal sinus contains fat, it normally appears brightly echogenic. The calyces are normally not visible. The medullary pyramids are hypoechoic. The renal parenchyma has uniformly low echogenicity, which is usually less than that of the adjacent liver and spleen (Fig. 19-9).Hydronephrosis
 In patients experiencing renal colic, ultrasound is used primarily to evaluate for the presence of hydronephrosis since the ureters are difficult to visualize with US. The stone search itself is almost always carried out by CT scanning (see Chapter 16).
In patients experiencing renal colic, ultrasound is used primarily to evaluate for the presence of hydronephrosis since the ureters are difficult to visualize with US. The stone search itself is almost always carried out by CT scanning (see Chapter 16). The typical appearance of obstructive uropathy is a dilated calyceal system. The echogenic renal sinus contains a dilated, fluid-filled, and therefore anechoic renal pelvis. The ureter may be dilated to the level of the obstructing stone. Severe hydronephrosis may distort the appearance of the kidney (Fig. 19-10).
The typical appearance of obstructive uropathy is a dilated calyceal system. The echogenic renal sinus contains a dilated, fluid-filled, and therefore anechoic renal pelvis. The ureter may be dilated to the level of the obstructing stone. Severe hydronephrosis may distort the appearance of the kidney (Fig. 19-10).Medical Renal Disease
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree