The following case sets have been designed to assess your overall knowledge in nuclear imaging. Each set contains 10 cases, and almost all sets have an example of central nervous system, thyroid, cardiac, respiratory, gastrointestinal, musculoskeletal, tumor, or abscess and positron emission tomography (PET) cases. This is a common review format. In addition, there are several questions regarding each case. You should be able to recognize most of the examinations, know the radiopharmaceutical used, understand the technique, give a differential diagnosis of one to three entities, and in some cases, discuss management. Table 1 in this set may help you differentiate and recognize different types of whole-body scans. By challenging yourself on all of the case sets, you will have covered many of the most common entities in nuclear medicine. Answers to all of the cases and additional questions are given after Case Set 7. If you have trouble with a case, go back to the chapter and specific text on that topic and review it. Good luck.

| Radiopharmaceutical | Liver | Spleen | GU | Bowel | Bone Marrow | Salivary | Thyroid | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 F-FDG | + | + | +++ | ++ Usually colon | + | + | +/− | Brain +++ Heart ++/− Larynx +/− Muscle +/− |
| 111 In-WBC | ++ | +++ | + | |||||
| 99m Tc-WBC | ++ | +++ | + | + | + | |||
| 67 Ga-citrate | ++ | + | + 0–1 day | +++Usually colon | + | + | Lacrimal +/− | |
| 123,131 I sodium iodide | + | ++ | ++ Stomach, colon | + | If present or remnant | Nasal + | ||
| 111 In-octreotide | ++ | +++ | +++ | + | + | |||
| 123,131 I-MIBG | + | ++ | + | + | + | Heart + Nasal + Lung + | ||
| 99m Tc-sulfur colloid | +++ | ++ | + | |||||
| 99m Tc-sestamibi | + | + | + | ++ | + | Heart ++ Gallbladder | ||
| 201 Tl-chloride | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | + | Muscle ++ Heart ++ Testis ++ |
Case 1.1
- 1.1a.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
- 1.1b.
If 370 MBq (10 mCi) of 99m TcO 4 − had been administered to the patient inadvertently instead of 99m Tc-MAG3, would it constitute a reportable “medical event”?
- 1.1c.
What is the difference in mechanism of renal excretion between DTPA and MAG3?

Case 1.2
- 1.2a.
What is the likely diagnosis?
- A.
Cortical atrophy with ventricular CSF reflux
- B.
Communicating arachnoid cyst
- C.
CSF leak
- D.
Ventricular shunt obstruction
- E.
Normal pressure hydrocephalus
- A.
- 1.2b.
What characteristics differentiate this from a normal study?
- 1.2c.
Identify the anatomy on these images.

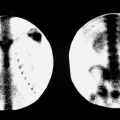
Case 1.3
- 1.3.
Regarding the images, which of the following is/are true?
- A.
The results may be due to improper energy window setting.
- B.
Energy peaking is typically done for every individual scan.
- C.
The energy window should be 20% and set at 160 keV.
- D.
A collimator defect was likely present on the posterior camera head.
- E.
The posterior camera head may be too far from the patient.
- A.

Case 1.10
- 1.10.
Regarding the image, which of the following is/are true?
- A.
The meter reading indicates that the package is likely damaged, and the delivery carrier and the NRC should be notified.
- B.
The radioactive II label means that this is a Type B package.
- C.
The limit for radiation dose at 1 meter from this package is 1 mrem (10 µSv) per hour.
- D.
A wipe test of the surface of this package is required upon receipt.
- E.
Packages are required to be monitored within 3 hours of receipt or within 3 hours of the next business day.
- A.

Case 2.3
- 2.3a.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A.
Regenerating nodule
- B.
Focal nodular hyperplasia
- C.
Hepatoma
- D.
Hemangioma
- E.
Recent hematoma
- A.
- 2.3b.
What other liver lesions may accumulate gallium?
- 2.3c.
What are appearances of hepatic adenoma and focal nodular hyperplasia on a 99m Tc-sulfur-colloid liver scan?

Case 2.4
- 2.4a.
What type of scan is this?
- 2.4b.
What is the diagnosis?
- A.
Bile leak
- B.
Free pertechnetate from poor radiopharmaceutical labeling
- C.
Biliary atresia
- D.
Choledochal cyst
- E.
Hepatitis
- A.
- 2.4c.
In an effort to keep radiation doses to children low, what administered activity should be given to this 2-kg infant?

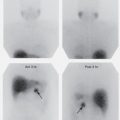
Case 2.6
- 2.6a.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A.
Fat emboli
- B.
Pneumonia
- C.
COPD
- D.
Metastases
- E.
Multiple thromboemboli
- A.
- 2.6b.
What category is this, according to modified PIOPED II criteria?
- 2.6c.
A large amount of central deposition on a 99m Tc-DTPA aerosol scan is an indication of what entity?

Case 2.9
- 2.9a.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
- 2.9b.
Is fine-needle aspiration biopsy warranted?
- 2.9c.
With what radiopharmaceutical was this scan performed?
- 2.9d.
In treating toxic MNG with 131 I, is the administered activity generally more or less than when treating Graves disease?