KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Urinary tract stone, urinary calculous disease, nephrolithiasis, ureterolithiasis, vesicolithiasis
- •
Macroscopic concretions of crystals in urinary system, sometimes mixed with proteins
Imaging
- •
US has 96% sensitivity, nearly 100% specificity for renal stones > 5 mm
- •
US is valuable for follow-up imaging, particularly in patients with renal colic & known renal stones or patients not improving on treatment for known stone
- •
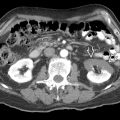
Virtually all stones are visible (including those radiolucent on KUB) on CT except pure matrix stones & protease inhibitor stones (e.g., indinavir, treatment of HIV)
- •
NECT is preferred imaging modality to confirm stone in adult patients with acute flank pain
- ○
Most accurate measurement technique on CT: Bone windows & magnification
- ○
- •
Choice of imaging modality follow-up is often based on visibility of stone on CT scout image
- •
In patients with BMI < 30, consider low-dose CT
- •
Dual-energy CT can differentiate urate stones from other types of stones with high accuracy
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Milk of calcium in small cyst
- •
Arterial calcifications
- •
Nephrocalcinosis
- •
Emphysematous pyelonephritis
Pathology
- •
Dependent on type of stone
Clinical Issues
- •
Size, number, location, evidence of obstruction or infection, & relevant anatomic findings (aberrant vasculature, distorted pelvicalyceal architecture, infundibular orientation) are all imaging findings that impact treatment
Scanning Tips
- •
US protocol: Drink 16-32 oz water prior to examination to fill bladder
- •
Always include bladder with special attention to UVJ
- •
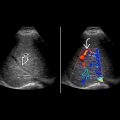
Twinkling artifact on color Doppler is useful to identify otherwise occult stone; more sensitive than acoustic shadowing but higher false-positive rate
 within the mid right kidney. Posterior acoustic shadowing
within the mid right kidney. Posterior acoustic shadowing  helps differentiate this stone from the surrounding sinus fat.
helps differentiate this stone from the surrounding sinus fat.
 with twinkling artifact
with twinkling artifact  and posterior acoustic shadowing
and posterior acoustic shadowing  .
.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree