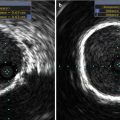
Fig. 32.1
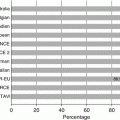
Incidence of structural valve degeneration (SVD) with surgical bioprosthetic valves
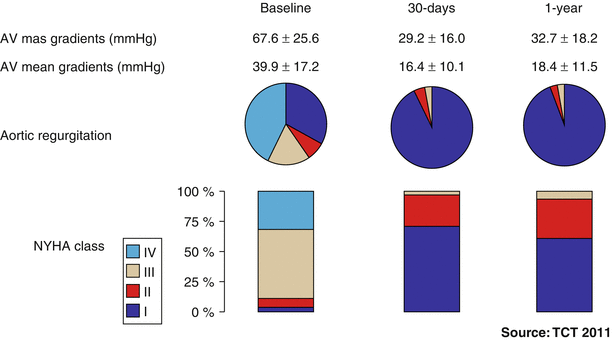
Fig. 32.2
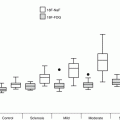
One-year outcome results from the Global Valve-in-Valve Registry (n = 78). AV aortic valve, NYHA New York Heart Association (Image courtesy of Dr Danny Dvir, Washington Hospital Center, Washington DC, USA)
It is recognized that the valve-in-valve procedure is technically challenging and requires appropriate case and device selection. Imaging plays a key role in all aspects of valve-in-valve implantation. Multidetector computed tomography (MDCT), echocardiography, and periprocedural angiography to evaluate the radiopaque surgical landmarks are all crucial for correct valve-in-valve sizing and positioning and thus, successful implantation. We will review imaging requirements for valve-in-valve implantation for failed surgical bioprostheses. Valve-in-valve implantation for failed or malpositioned transcatheter valves is a separate topic and not discussed.
Surgical Valves
Bioprosthetic surgical valves have consistent, reproducible leaflet kinetics as the leaflets are mounted in a rigid framework. The wide variety of surgical valves available can be broadly classified into stented and stentless devices (Tables 32.1 and 32.2). These groups have unique features that must be considered for valve-in-valve sizing and positioning. Conventional bioprosthetic valves incorporate bovine or porcine pericardium incorporated into a stent frame or stentless conduit.
Table 32.1
Structural dimensions of stented bioprosthetic valves
Valve label size | Valve type/model (manufacturer) | Sewing ring external diameter, mm | Stent outer diameter, mm | Stent internal diameter, mm | Profile height, mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
18 | Soprano (Sorin Biomedica) | 26 | 21 | 17.8 | 12 |
19 | Magna (Edwards Lifesciences) | 24 | 19 | 18 | 13 |
Perimount (Edwards Lifesciences) | 26 | 19 | 18 | 14 | |
Mosaic (Medtronic) | 25 | 19 | 17.5 | 13.5 | |
Hancock Ultra (Medtronic) | 24 | 19 | 17.5 | 14 | |
Mitroflow (Sorin Biomedica) | 21 | 18.6 | 15.4 | 11 | |
Trifecta (St. Jude Medical) | 24 | 19 | 17 | 15 | |
Epic Supra/Biocor Supra (St. Jude Medical) | 25 | 19 | 19 | 14 | |
20 | Soprano (Sorin Biomedica) | 28 | 23 | 19.8 | 14 |
Aspire (Vascutek Terumo) | 23 | 20 | 18.2 | 16 | |
21 | Magna (Edwards Lifesciences) | 26 | 21 | 20 | 15 |
Perimount (Edwards Lifesciences) | 29 | 21 | 20 | 15 | |
Mosaic/Hancock II (Medtronic) | 27 | 21 | 18.5 | 15 | |
Hancock/Hancock Ultra (Medtronic) | 26 | 21 | 18.5 | ||
Mitroflow (Sorin Biomedica) | 23 | 20.7 | 17.3 | 13 | |
Trifecta (St. Jude Medical) | 26 | 21 | 19 | 16 | |
Epic/Biocor (St. Jude Medical) | 25 | 21 | 19 | 14 | |
Aspire (Vascutek Terumo) | 24 | 21 | 19.2 | 16 | |
22 | Soprano (Sorin Biomedica) | 30 | 25 | 21.7 | 15 |
23 | Magna (Edwards Lifesciences) | 28 | 23 | 22 | 16 |
Perimount (Edwards Lifesciences) | 31 | 23 | 22 | 16 | |
Mosaic/Hancock II (Medtronic) | 30 | 23 | 20.5 | 16 | |
Hancock/Hancock Ultra (Medtronic) | 28 | 23 | 22 | ||
Mitroflow (Sorin Biomedica) | 26 | 22.7 | 19 | 14 | |
Trifecta (St. Jude Medical) | 28 | 23 | 21 | 17 | |
Epic/Biocor (St. Jude Medical) | 27 | 23 | 21 | 15 | |
Aspire (Vascutek Terumo) | 26 | 23 | 21 | 17 | |
24 | Soprano (Sorin Biomedica) | 32 | 27 | 23.7 | 16 |
25 | Magna (Edwards Lifesciences) | 28 | 23 | 22 | 17 |
Perimount (Edwards Lifesciences) | 31 | 23 | 22 | 17 | |
Mosaic/Hancock II (Medtronic) | 33 | 25 | 22.5 | 17.5 | |
Mosaic Ultra/Hancock I Ultra (Medtronic) | 30 | 25 | 22.5 | ||
Mitroflow (Sorin Biomedica) | 29 | 25.1 | 21 | 15 | |
Trifecta (St. Jude Medical) | 31 | 25 | 23 | 18 | |
Epic/Biocor (St. Jude Medical) | 29 | 25 | 23 | 16 | |
Epic Supra (St. Jude Medical) | N/A | 25 | 25 | ||
Aspire (Vascutek Terumo) | 28 | 25 | 23 | 18 | |
26 | Soprano (Sorin Biomedica) | 35 | 29 | 25.6 | 19 |
27 | Magna (Edwards Lifesciences) | 32 | 27 | 26 | 18 |
Perimount (Edwards Lifesciences) | 35 | 27 | 26 | 18 | |
Mosaic/Hancock II (Medtronic) | 36 | 27 | 24 | 18.5 | |
Mosaic Ultra/Hancock II Ultra (Medtronic) | 32 | 27 | 24 | ||
Mitroflow (Sorin Biomedica) | 31 | 27.3 | 22.9 | 16 | |
Trifecta (St. Jude Medical) | 33 | 27 | 25 | 19 | |
Epic/Biocor (St. Jude Medical) | 31 | 27 | 25 | 17 | |
Aspire (Vascutek Terumo) | 30 | 27 | 25 | 18 | |
28 | Soprano (Sorin Biomedica) | 38 | 31 | 27.6 | 19 |
29 | Magna (Edwards Lifesciences) | 34 | 29 | 28 | 19 |
Perimount (Edwards Lifesciences) | 37 | 29 | 28 | 19 | |
Mosaic/Hancock II (Medtronic) | 39 | 29 | 26 | 20 | |
Mosaic Ultra/Hancock II Ultra (Medtronic) | 34 | 29 | 26 | ||
Mitroflow (Sorin Biomedica) | 33 | 29.5 | 24.7 | 16 | |
Trifecta (St. Jude Medical) | 35 | 29 | 27 | 20 |
Table 32.2
Structural dimensions of stentless bioprosthetic valves
Valve label size | Bioprosthesis | Manufacturer | Outer diameter, mm | Internal diameter, mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
19 | Freestyle | Medtronic | 19 | 16 |
Prima Plus | Edwards Lifesciences | 19 | 16 | |
3 F Therapeutics | ATS Medical | 19 | 17 | |
Pericarbon Freedom | Sorin Biomedica | 19 | 17 | |
21 | Freestyle | Medtronic | 21 | 18 |
Prima Plus | Edwards Lifesciences | 21 | 18 | |
3 F Therapeutics | ATS Medical | 21 | 19 | |
Toronto SPV | St. Jude Medical | 21 | 18 | |
Pericarbon freedom | Sorin Biomedica | 21 | 19 | |
23 | Freestyle | Medtronic | 23 | 20 |
Prima Plus
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|