Wegener Granulomatosis, Airways
Melissa L. Rosado-de-Christenson, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Terminology
Systemic necrotizing granulomatous vasculitis of small to medium-sized vessels
May produce tracheobronchial stenosis
Imaging Findings
Tracheal wall thickening/stenosis
Frequent subglottic involvement
Typically 2-4 cm in length
Circumferential or asymmetric involvement
Bronchial wall thickening/stenosis
Focal or long segment
Associated atelectasis &/or consolidation
Distal airway involvement
Peribronchovascular thickening
Bronchiectasis
Laryngeal/supraglottic stenosis
Top Differential Diagnoses
Tracheobronchial Neoplasm
Amyloidosis
Relapsing Polychondritis
Acquired Tracheal Stenosis
Pathology
Necrotizing vasculitis and granulomatosis
Subglottic stenosis, tracheobronchial stenosis, and ulcerating tracheobronchitis
Clinical Issues
Dyspnea, wheezing, and stridor
Asymptomatic, incidental diagnosis at bronchoscopy
Diagnostic Checklist
Airway involvement may be presenting manifestation of WG and may occur without other features of WG
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations and Synonyms
Wegener granulomatosis (WG)
Definitions
Wegener granulomatosis = systemic necrotizing granulomatous vasculitis of small to medium-sized vessels
Classic WG = triad of upper respiratory tract, lung, and renal vasculitis; other organs may be affected
Limited WG = pulmonary vasculitis without upper respiratory tract or renal involvement; other organs may be affected
American College of Rheumatology criteria distinguishes WG from other vasculitides
≥ 2 abnormal urinary sediments (red cell casts)
Oral ulcers or nasal discharge, hemoptysis
Granulomatous inflammation on lung biopsy
Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)
Antibodies present in serum of patients with WG
Cytoplasmic staining pattern of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (c-ANCA)
Diffuse granular staining pattern; ANCA binds to antigenic targets in neutrophil cytoplasm
Proteinase 3 (PR3); most common cytoplasmic antigenic target
PR3-ANCA; 80-90% sensitivity and 95% specificity in generalized active WG
Perinuclear-staining pattern of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (p-ANCA)
Staining of antigen targets aberrantly positioned around cell nucleus
Associated with vasculitis; may be seen in active WG
IMAGING FINDINGS
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
Large airway focal or diffuse stenosis
Association with multifocal bilateral lung nodules &/or consolidations that may exhibit cavitation
Patient position/location: Subglottic trachea, bronchi
Size: Length of airway stenosis, typically 2-4 cm
Morphology: Circumferential soft tissue thickening of airway wall
CT Findings
Airway lesions on CT in up to 40% of WG patients
Central airway abnormalities in 30%
Segmental/subsegmental airway wall thickening ± stenosis in up to 73%
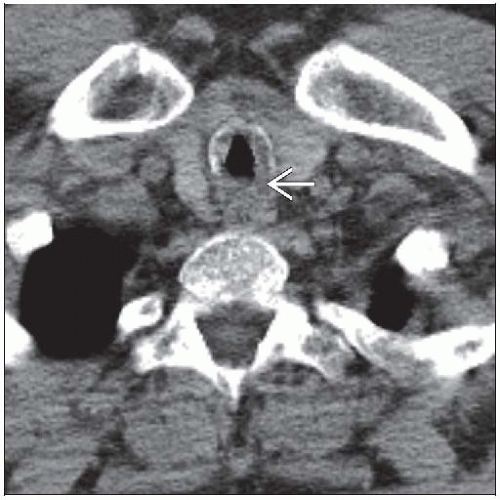
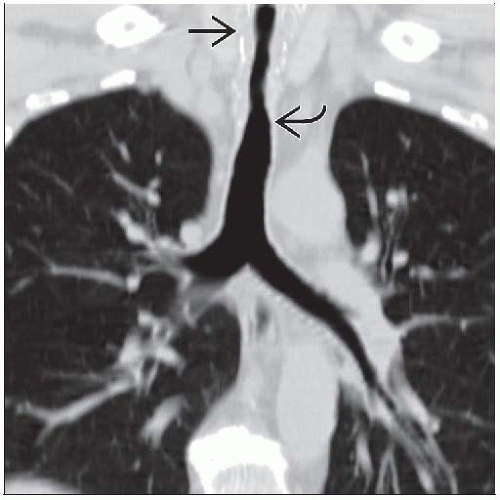
Tracheal wall thickening/stenosis
Typically subglottic; may affect vocal cords
Up to 23% of patients with active WG
May occur without other features of active WG
May be presenting manifestation of WG
Typically focal, 2-4 cm long
Smooth or irregular soft tissue thickening of airway wall; may interrupt tracheal cartilage rings
Abnormal cartilage thickening or calcification
Circumferential or asymmetric airway involvement
Bronchial wall thickening/stenosis
Focal or long segment involvement
Unilateral or bilateral
Main, lobar, segmental, subsegmental bronchi
May obstruct airway lumen with resultant consolidation/atelectasis
Distal airway involvement
Peribronchovascular thickening
Bronchiectasis
Laryngeal/supraglottic stenosis
Associated pulmonary findings
Atelectasis from central airway obstruction
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree