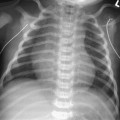
CASE 33 A term newborn presented with respiratory distress at birth and meconium-stained fluid. Figure 33A Figure 33B Frontal (Fig. 33A) and lateral (Fig. 33B) radiographs of a term newborn with meconium aspiration syndrome reveals bilateral combined multifocal air space, and nodular and interstitial disease in large volume lungs. The radiographs show diffuse hyperinflation and patchy areas of mixed emphysema and atelectasis, with symmetric or asymmetric bilateral nodular infiltrates. Note the moderate-sized left tension pneumothorax (manifestation of air-block phenomenon). This is commonly seen secondary to the requirement for pressure ventilation in a child with significant large and small airway obstruction by the meconium plugs (Fig. 33A). Figure 33C AP chest radiograph demonstrates bilateral pneumothoraces. Figure 33D AP chest radiograph illustrates the common pattern of combined air space and interstitial changes in this process. Meconium aspiration syndrome
Clinical Presentation
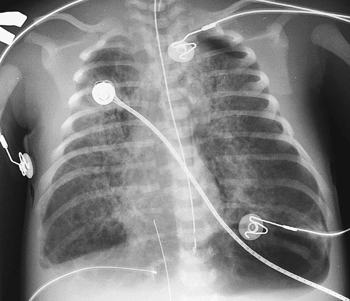

Radiologic Findings


Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree