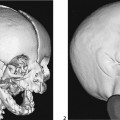
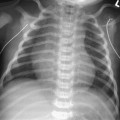
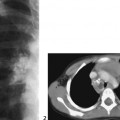
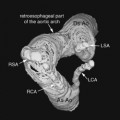
CASE 51 A newborn presents with respiratory distress and cyanosis. Figure 51A A frontal chest radiograph (Fig. 51A1) shows situs solitus and levocardia. The heart is displaced to the left side in association with collapse of the left lower lobe and lingular segment of the left upper lobe. The right lung is hyperinflated. On follow-up examination (Fig. 51A2), the left lower lobe is expanded, but there is a new area of segmental collapse in the left upper lung. Figure 51B Contrast-enhanced CT angiogram. AsAo, ascending aorta; DsAo, descending aorta; LMB, left main bronchus; LPA, left pulmonary artery; MPA, main pulmonary artery; RMB, right main bronchus; RPA, right pulmonary artery; RVOT, right ventricular outflow tract. Tetralogy of Fallot with absent pulmonary valve syndrome. A contrast-enhanced CT image (Fig. 51B) shows markedly dilated main, right, and left pulmonary arteries in the mediastinum. The left main bronchus is compressed between the dilated pulmonary artery and the spine. The right main bronchus also shows a lesser degree of compression. The hyperinflated right lung is herniated into the left thorax, whereas the left lower lobe shows collapse. Cyanotic newborn with hyperinflated lungs or mixture of lobar or segmental emphysema and collapse.
Clinical Presentation

Radiologic Findings

Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Clinical Findings
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree