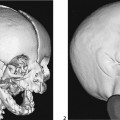
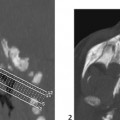
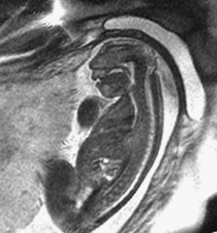
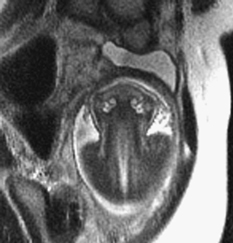
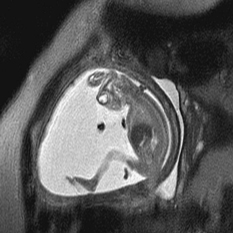
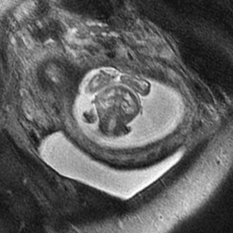
CASE 11 Fetal MRI was requested following abnormal prenatal ultrasound in two different patients. Figure 11A Figure 11B Figure 11C Figure 11D Anencephaly and exencephaly are primarily morphologic diagnoses, typically recognized by fetal ultrasonography and better depicted by fetal MRI. A series of views from prenatal MRI study shows the typical features of anencephaly. There is total absence of the cerebrum and calvarium superior to the orbits and the misshaped skull base (Figs. 11A and 11B). The fetal MRI of exencephaly (Figs. 11C and 11D) demonstrates that the hemispheres are extruded from the open skull and floating into the amniotic fluid. Exencephaly/anencephaly sequence Anencephaly/exencephaly sequence is a type of neural tube defect related to myelomeningocele (Chiari II). A high serum a-feto protein may be the first clue during early pregnancy. Fetal ultrasound is confirmatory. There is a variable reported frequency of 0.5 to 10 per 1000 live births, with a strong female predominance. The incidence of anencephalic births is decreasing due to maternal folate administration and prenatal recognition. Anencephaly has been linked with folate deficiency and the methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) unfavorable genotype or folate antagonists. Clomiphene citrate ovulation induction is another possible factor. Familial cases have been reported. Chromosomal abnormalities (aneuploidy) are present in ~2%, in particular trisomy 2p.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Etiology
Embryology
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree