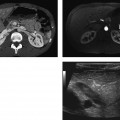
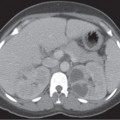
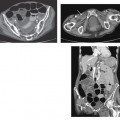
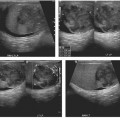
CASE 123 A 77-year-old man presents with right scrotal swelling and urinary retention. Fig. 123.1 (A–F) Axial noncontrast CT images of the pelvis show herniation of the urinary bladder into the right inguinal canal with nearly the entirety of the bladder herniated into the scrotum. Axial and coronal noncontrast computed tomography (CT) images show herniation of the urinary bladder into the right inguinal canal with nearly the entirety of the bladder herniated into the scrotum (Fig. 123.1). Urinary bladder hernia One to 3% of all inguinal hernias involve the urinary bladder. Most bladder hernias involve the inguinal and femoral canals, although herniation through ischiorectal, obturator, and other abdominal wall defects has also been described. Herniation of the bladder can be within a true hernia sac; however, bladder herniation is most commonly paraperitoneal in location, with the bladder remaining extraperitoneal and medial to a true inguinal hernia sac.
Clinical Presentation
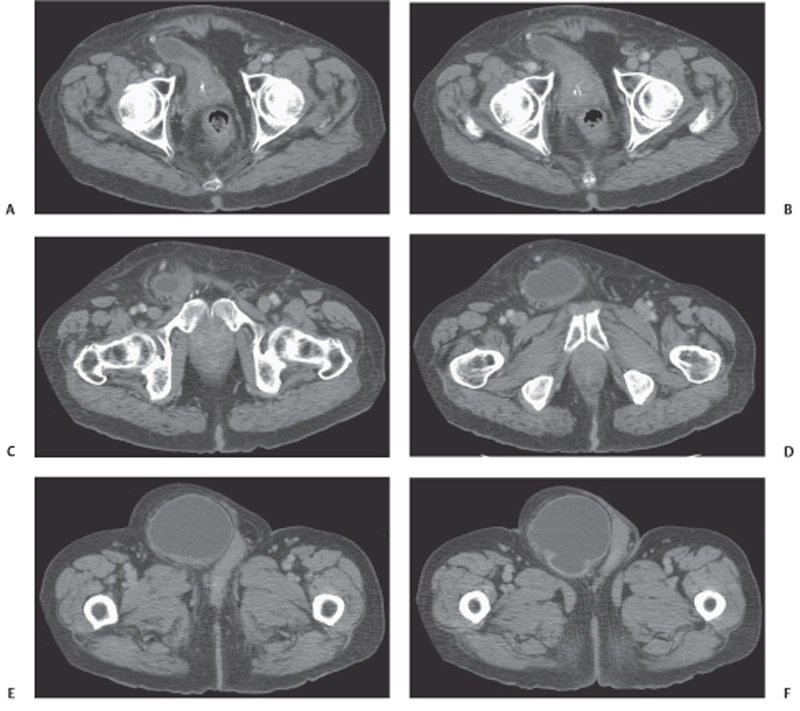
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree