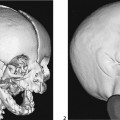
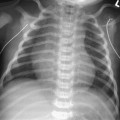
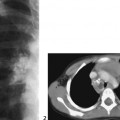
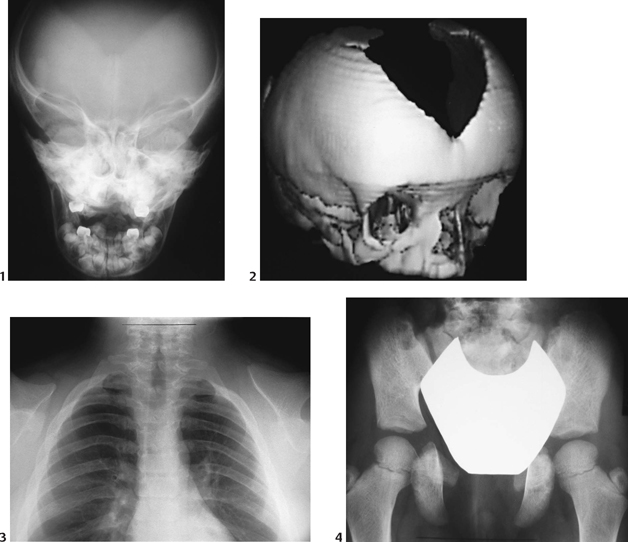
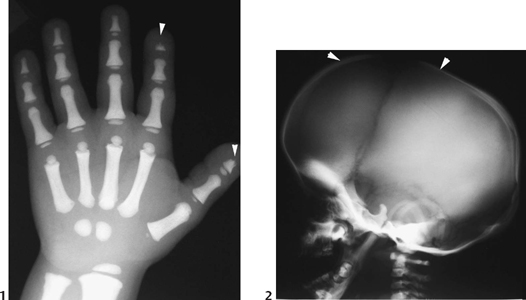
CASE 124 A 7-year-old child presents with abnormal dentition, large anterior fontanelle, and hypermobile scapulae. Figure 124A Anteroposterior radiograph (Fig. 124A1) of the cranium demonstrates a large, patent anterior fontanelle, along with a partially patent metopic suture. Three-dimensional CT (Fig. 124A2) confirms abnormally enlarged anterior fontanelle and partially patent metopic suture. Posteroanterior chest radiograph (Fig. 124A3) reveals extremely hypoplastic clavicles, with a slight proximomedial translation of the scapulae. Posteroanterior pelvis radiograph (Fig. 124A4) demonstrates hypoplastic ischia and pubic rami. The iliac wings are small and narrow. Acetabular roofs are horizontal, and the symphysis pubis is widened. Figure 124B Patient with pyknodysostosis. Note marked osteosclerosis and distal tapering of tufts (acro-osteolysis; 1, arrowheads). Lateral radiograph of calvarium shows large anterior fontanelle (2, arrowheads), osteosclerosis, and abnormal mandibular angle. Cleidocranial dysplasia Formerly termed cleidocranial dysostosis, this entity is now more properly termed cleidocranial dysplasia to reflect the fact that this condition is a generalized skeletal dysplasia. Cleidocranial dysplasia is an autosomal dominant condition characterized by defective midline ossification, including abnormalities of the calvarium, dentition, clavicles, sternum, and pelvis. Incidence is 1 per 1,000,000 live births.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree