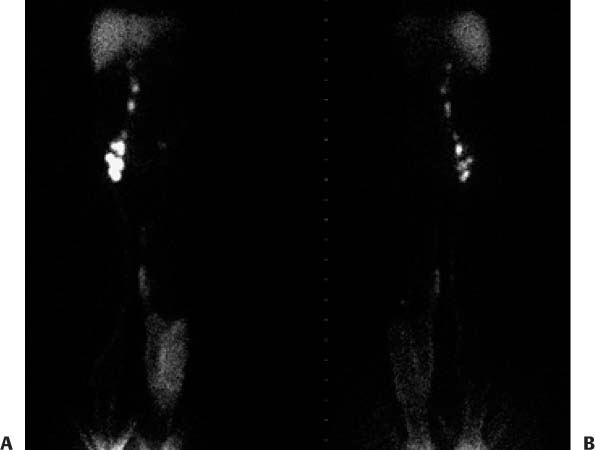
CASE 129 A 42-year-old woman underwent pelvic surgery 2.5 years ago. There has been a gradual onset of left lower extremity edema without a venous explanation. Lymphatic drainage is to be evaluated. Fig. 129.1 • Filtered (0.22 μm filter) sulfur colloid labeled with 99mTc-sulfur colloid is administered at a concentration of 10 mCi (370 MBq)/mL and at a dose of 0.5 mCi (18.5 MBq) per injection site. • Administer two 0.05-mL intradermal injections of 99mTc-sulfur colloid into the dorsum (as opposed to the web space) of each foot with sterile technique. The contralateral extremity is injected to provide a comparison. The patient is then asked to go up and down a flight of stairs to aid lymphatic drainage from the injection site. • Successive anterior and posterior whole-body images are acquired at 8 cm/min up to the level of the chest, with the injection sites left out of the field of view. Images are obtained over the first 90 minutes after the injection until the lymph vessels and nodal groups are visualized up to the cisterna chyli and until the liver is visualized. Delayed views (2–3 hours after the injection) are also obtained to assess for dermal backflow, or “cutaneous flare.” This is important in the diagnosis of lymphedema and may not be evident on the earlier set of images. • The end point of an examination occurs when the clinical question has been answered. Delayed anterior (Fig. 129.1A) and posterior (Fig. 129.1B) whole-body views show a normal right lower extremity lymphoscintigraphy. Visualization of the deep lymphatic vessels along the right lower extremity is followed by filling of the right inguinal and iliac nodes and progression of the tracer into the right para-aortic nodal chain up to the level of the cisterna chyli. The liver is also visualized. There is only faint visualization of the deep lymphatic vessels in the left lower extremity, and diffuse cutaneous flare is seen from the knee to the ankle. Two areas of more focal flare are also seen in the medial aspect of the left thigh. There is only faint visualization of an inguinal lymph node and no further progression of activity beyond the inguinal region. The posterior view shows a left popliteal lymph node. • Low plasma osmotic pressure
Clinical Presentation
Technique
Image Interpretation
Differential Diagnosis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree