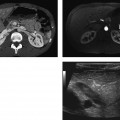
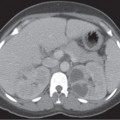
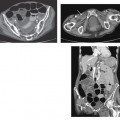
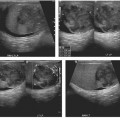
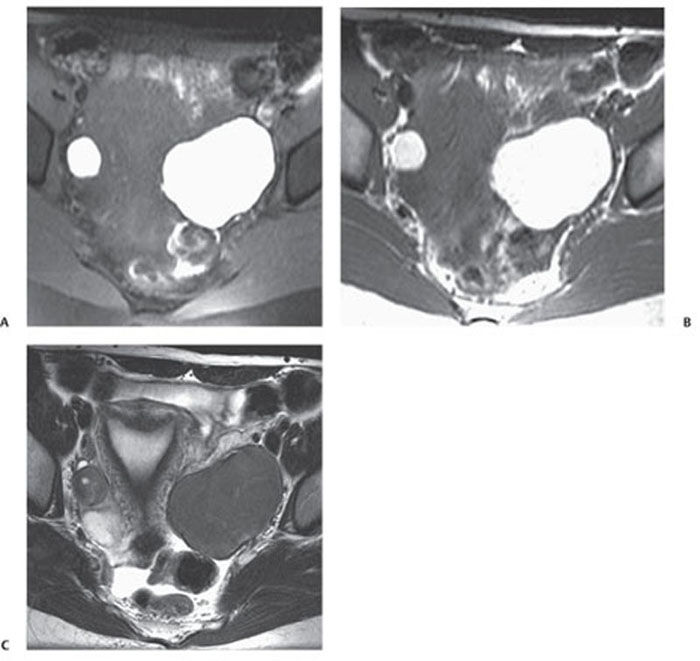
CASE 135 A 31-year-old woman presents with severe pelvic pain and a history of dysmenorrhea. Fig. 135.1 Axial MR T1-weighted images (A) with and (B) without fat saturation demonstrate bilateral T1 hyperintense ovarian lesions, which show relative hypointensity on (C) an axial T2-weighted image consistent with multiple endometriomas. Axial magnetic resonance (MR) T1-weighted images with and without fat saturation (Fig. 135.1) demonstrate bilateral T1 hyperintense ovarian lesions, which show relative hypointensity on an axial T2-weighted image consistent with multiple endometriomas. Endometrioma (chocolate cyst) Endometriosis is a gynecologic disorder, typically occurring in women of childbearing age (mean age 25–29 years), defined by the presence of ectopic endometrial tissue mostly located in the ovaries (endometrioma), fallopian tubes, cervix, vagina, uterosacral or broad ligaments, and cul-de-sac of Douglas. The term adenomyosis refers to the presence of endometrial tissue within the myometrium, but it is considered a distinct clinical entity according to the different symptoms, pathophysiology, and epidemiology. The gastrointestinal (GI) tract represents the most common extrapelvic site of endometriosis, but endometriosis has been reported in the abdominal wall (including laparoscopic scars), bladder, kidneys, spleen, gallbladder, nasal mucosa, pleura, lung parenchyma, and central nervous system. These lesions vary in size, ranging from microscopic implants to large lesions. The main risk factors for endometriosis are positive familiar history, hypermenorrhea, early age of menarche, and delayed childbearing. Patients may be completely asymptomatic or present with infertility (30–50% of cases), severe pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, and dyschezia (pain during defecation). Other symptoms are dependent on the site of disease and may include cyclic hemoptysis and catamenial pneumothorax if the chest is involved, for example, or urinary urgency, hematuria, and frequent urination in case of bladder involvement. Seizures, cyclic headaches, and subarachnoid hemorrhages have been described with central nervous system lesions.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Clinical Findings
Complications
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree