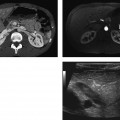
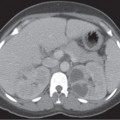
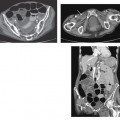
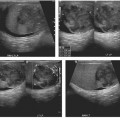
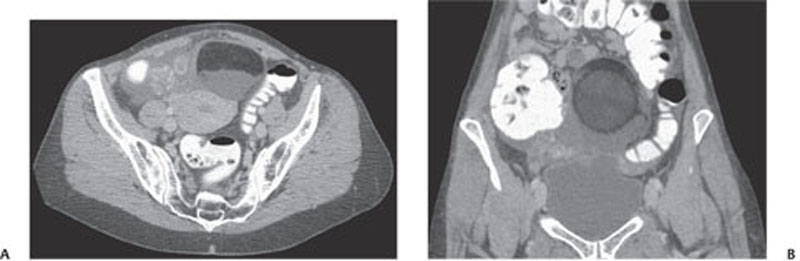
CASE 137 A 26-year-old woman presents with acute, severe pelvic pain, nausea, and vomiting. Fig. 137.1 (A) Axial contrast-enhanced CT image demonstrates a heterogeneous, well-defined lesion centered in the midpelvis with a predominantly fat content and a fluid–fat level consistent with a dermoid; the right ovary is in close proximity to this lesion and appears ill-defined and edematous when compared with the contralateral side. These findings are highly suspicious for ovarian torsion. (B) Coronal CT image of the pelvis better emphasizes the size and location of the dermoid, as well as the edema and fluid collection surrounding the affected right ovary. Axial and coronal computed tomography (CT) images of the abdomen obtained after administration of contrast (Fig. 137.1) show a heterogeneous density mass in the midpelvis, with mixed fat and soft tissue density. Adjacent and to the right of this mass there is an ill-defined soft tissue density, likely representing an edematous and enlarged right ovary. The left ovary appears otherwise normal. Adnexal torsion secondary to ovarian dermoid Ovarian torsion is an uncommon but significant cause of lower abdominal pain, occurring at any age but mostly in the early reproductive years. Its incidence is slightly higher in developed countries as a consequence of ovarian stimulation for infertility, although other causative factors should be considered. This condition is caused by the torsion of the ovary and/or fallopian tube around the vascular pedicle, resulting in vascular compromise; a delayed diagnosis may lead to infarction of the ovary. Prompt identification of ovarian torsion at imaging is therefore mandatory for radiologists. Clinical presentation is often nonspecific. Patients experience severe acute abdominal pain, usually over the involved side and radiating to the back and pelvis, as well as nausea, vomiting, and fever.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Clinical Findings
Complications
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree