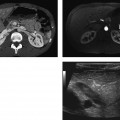
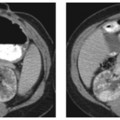
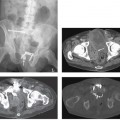
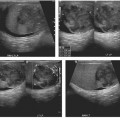
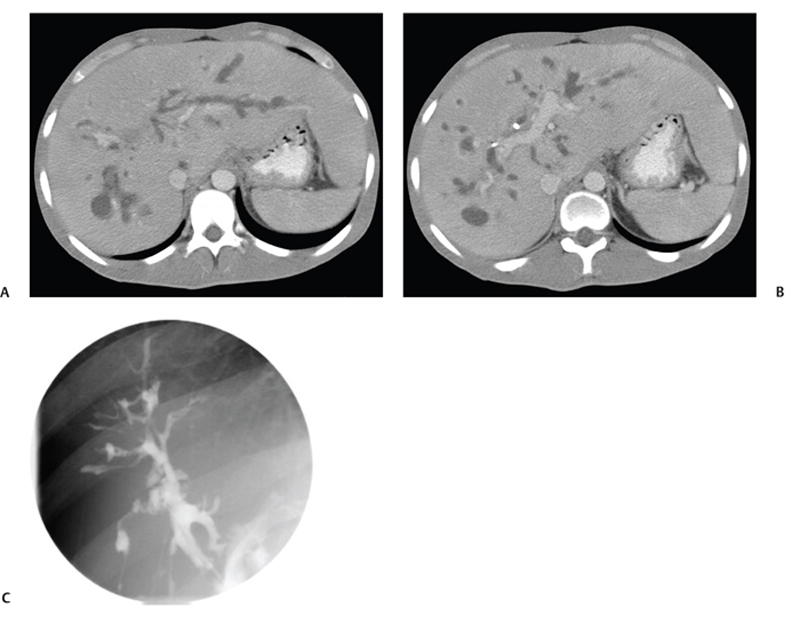
CASE 21 A young man presents with jaundice, fever, generalized malaise, and right upper quadrant pain. Fig. 21.1 (A,B) Axial contrast-enhanced CT images show irregularly dilated intrahepatic bile ducts with no focal mass lesion seen. (C) Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography shows abnormal arborization of intrahepatic bile ducts associated with multifocal strictures and irregularly ductal dilatation. Axial contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) images show irregularly dilated intrahepatic bile ducts with no focal mass lesion seen. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) shows abnormal arborization of the intrahepatic bile ducts associated with multifocal strictures and irregularly ductal dilatation (Fig. 21.1). Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) Primary sclerosing cholangitis is a chronic liver disease characterized by inflammation, destruction, and fibrosis of the intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts that leads to cirrhosis of the liver. It is most commonly seen in men, and 70% of patients are younger than 45 years.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Clinical Findings
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree