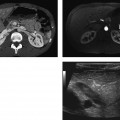
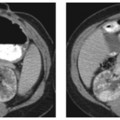
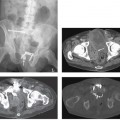
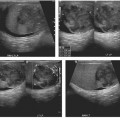
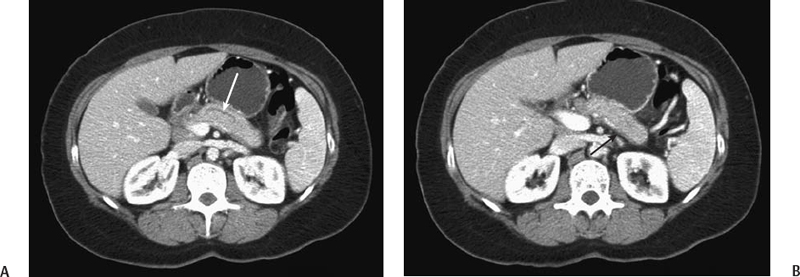
CASE 28 A 46-year-old man presents with abdominal pain and weight loss. Fig. 28.1 (A,B) Axial contrast-enhanced axial abdominal CT scan reveals mild swelling and enlargement of the pancreatic parenchyma with irregular dilatation of the main pancreatic duct (white arrow). The parenchyma shows loss of the normal lobulated contour. There is also a rind of soft tissue seen surrounding the parenchyma (black arrow). Abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan (Fig. 28.1) shows moderate diffuse enlargement and swelling of the pancreatic parenchyma; the main pancreatic duct is tortuous and mildly dilated. No calcifications, intraductal stones, peripancreatic fluid collections, mesenteric fat stranding, or lymphoadenopathy are present. Autoimmune pancreatitis
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree