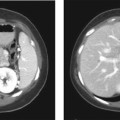
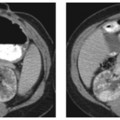
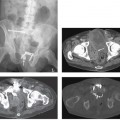
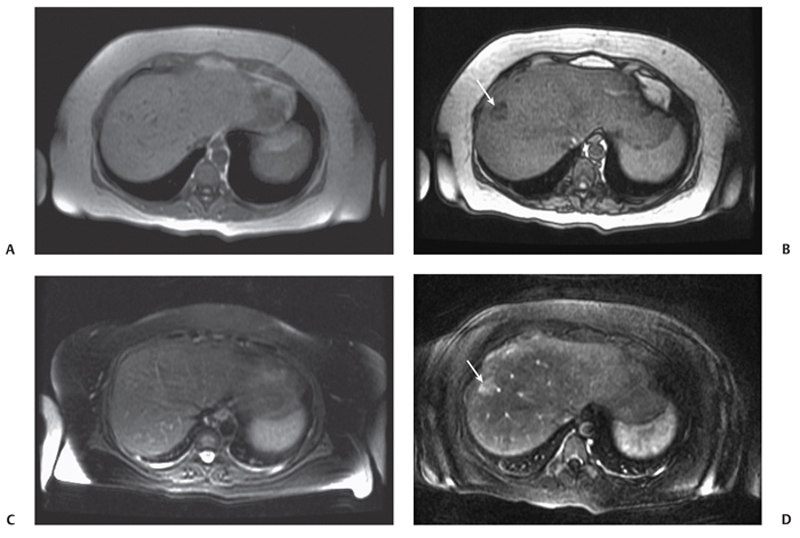
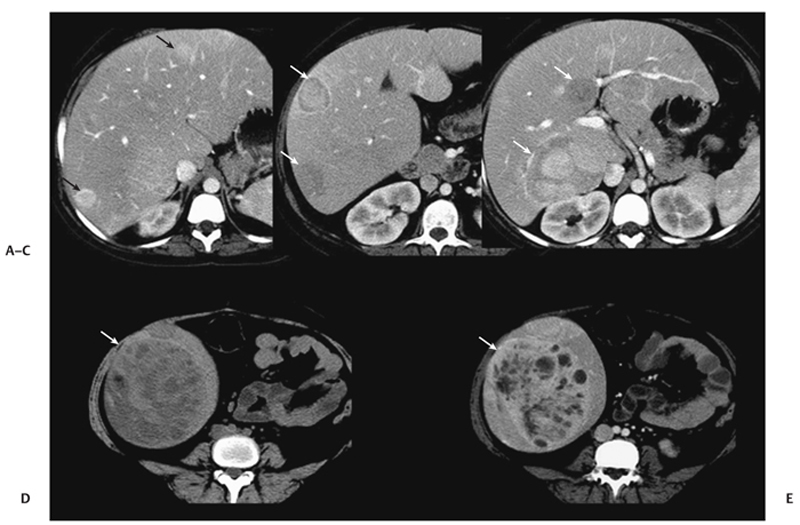
CASE 3 A 38-year-old woman presents with mild right upper quadrant pain. Fig. 3.1 Hepatic adenoma. (A) Gradient echo in-phase T1-weighted image fails to delineate the lesion. (B) On the out-of-phase image, there is signal dropout within the lesion (arrow), indicating the presence of intralesional fat. (C) The lesion is isointense on the T2-weighted image. (D) There is arterial enhancement seen in the lesion (arrow) with gadolinium. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the liver shows an isointense lesion on T2-weighted image with signal drop on the out-of-phase gradient echo sequence and showing brisk homogenous enhancement on the arterial phase images (Fig. 3.1). Liver adenoma Hepatic adenomas are uncommon benign neoplasms, mostly occurring in young women with a history of oral contraceptive use. Although typically solitary, multiple hepatic adenomas have been described in patients with glycogen storage disease and adenomatosis (Fig. 3.2); the latter is a distinct pathologic entity defined by the presence of more than 10 hepatic adenomas in patients without known risk factors. Adenomatosis is encountered both in men and women and is more often associated with impaired liver function and hepatic enzyme abnormalities (elevated level of alkaline phosphatase). The histology of hepatic adenomas consists of disorganized cords of hepatocytes without biliary ducts or portal areas. Kupffer cells may be present in small number but are not functional. Fig. 3.2 Multiple adenomas in a patient with glycogen storage disease. (A–E) Contrast-enhanced CT images show multiple enhancing adenomas (arrows) within the liver.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Clinical Findings
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree