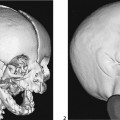
CASE 30 A 3-year-old child presents to the hospital with high fever and difficulty swallowing. She has a 5-day history of preexisting upper respiratory tract infection. Figure 30A Figure 30B Lateral neck radiograph demonstrates prevertebral/retropharyngeal space soft tissue swelling, which bulges into the normally sharp posterior pharyngeal tissues and piriform fossae (Fig. 30A). Axial CT reveals low soft tissue density in retropharyngeal space between the airway and the vertebral column, with a partial ring enhancement/thickening of the regional tissues (Figs. 30B1, arrows, and 30B2). Retropharyngeal cellulitis Retropharyngeal cellulitis and abscess usually occur in the age range of 6 months to 3 years. The retropharyngeal lymph nodes drain to the nasopharynx, middle ear, and tonsils. Bacterial superinfection of a previous viral infection in the nasopharyngeal soft tissues can result in inflammation in retropharyngeal soft tissues. Less commonly, the infection may occur from direct, foreign body penetration of the posterior pharynx.
Clinical Presentation
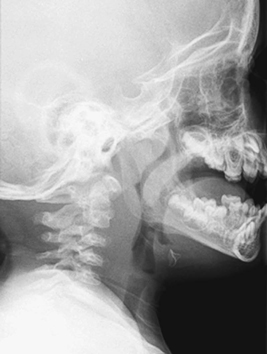
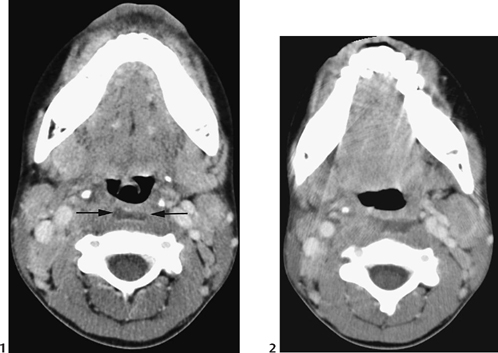
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Clinical Findings
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree