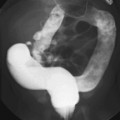
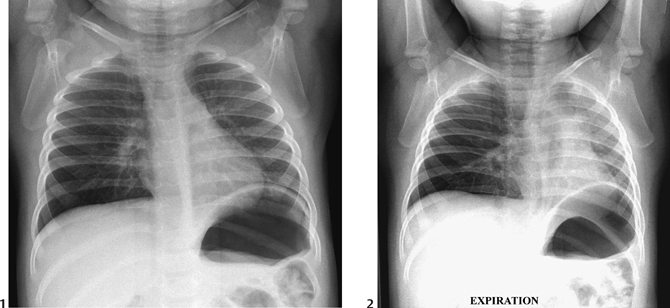
CASE 31 An afebrile 18-month-old presents with acute onset of a cough, respiratory distress, and wheezing. Figure 31A Conventional chest radiograph performed in appropriate inspiration demonstrated subtle asymmetric lucency, most obvious at the right base (Fig. 31A1). Mild hyperinflation of the right upper lobe also is seen with a slight shift of the mediastinal structures into the left hemithorax. Expiratory frontal view (Fig. 31A2) demonstrates overt mediastinal shift to the left secondary to extensive right-sided air trapping, the result of an aspirated piece of hamburger. Foreign body aspiration; aspiration of a piece of hamburger Although foreign body aspiration can occur at any age, the peak age range is between 9 months and 4 years of age, when children are most likely to explore their surroundings with their mouth. The radiographic diagnosis of foreign body aspiration requires a high index of suspicion that must be maintained when imaging children’s lungs. It is noteworthy that studies have shown that up to 20% of cases present with no choking episode (Hoeve et al), and up to 30% of cases may present to medical care more than a week after the episode of aspiration (Kim et al). Both the clinician and the radiologist must, therefore, have a low threshold for considering the utility of expiratory films to demonstrate focal air trapping.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Clinical Findings
Imaging Findings
RADIOGRAPHY
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree