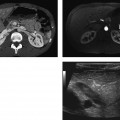
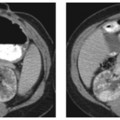
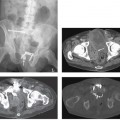
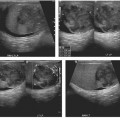
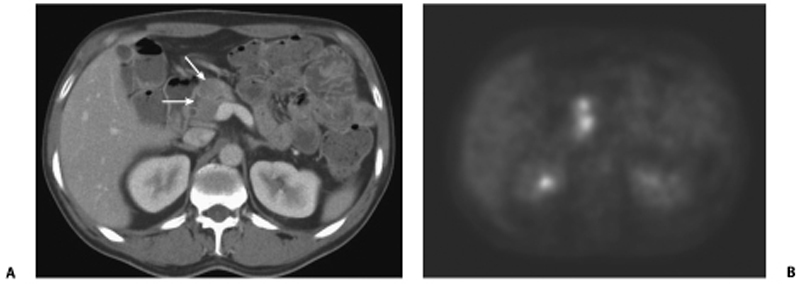
CASE 37 A 70-year-old Caucasian man presents with 2 months’ history of fullness of the stomach, 6 lb (2.7 kg) weight loss, and recent yellowish discoloration of the eyes and skin. Fig. 37.1 (A) Axial contrast-enhanced CT image shows a subtle hypoattenuating lesion (arrows) in the head of the pancreas with no significant common duct dilatation. The portal vein is patent. (B) Axial 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG PET) image in the same patient shows FDG uptake within the lesion. An ill-defined hypoattenuating mass is seen in the head of the pancreas (Fig. 37.1) without proximal common bile duct dilatation. There is very little mass effect due to the lesion. A corresponding positron emission tomography (PET) image in the same location shows 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) avidity of the lesion. Primary pancreatic lymphoma (non-Hodgkin type) Pancreatic lymphoma accounts for < 0.5 to 1.0% of cases of total pancreatic neoplasms. With the increasing population of people with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), it is becoming increasingly common.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree