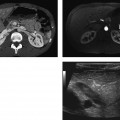
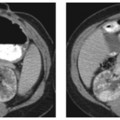
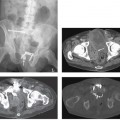
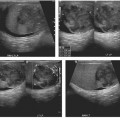
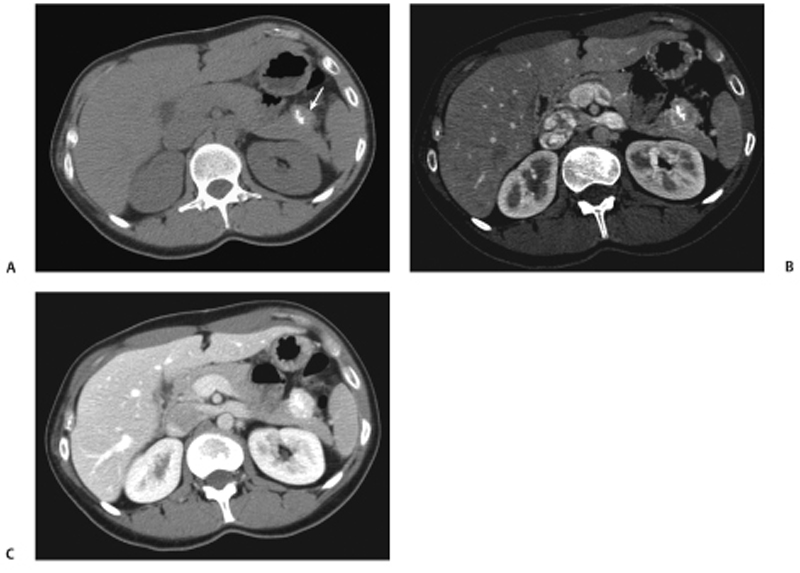
CASE 38 A 35-year-old woman presents with nonspecific abdominal pain. Fig. 38.1 (A) Axial noncontrast CT image shows an exophytic lesion arising from the tail of the pancreas (arrow) with eccentric calcification. (B) The lesion shows early arterial enhancement and continues to stay enhanced on the (C) portal venous-phase image. Axial noncontrast computed tomography (CT) image (Fig. 38.1A) shows an exophytic lesion arising from the tail of the pancreas with eccentric calcification. The lesion shows early arterial and sustained enhancement on the contrast-enhanced series (Fig. 38.1B,C). Nonfunctioning neuroendocrine tumor of the pancreas Nonfunctioning neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas are rare slow-growing tumors with a more indolent natural history compared with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. They constitute the majority of islet cell tumors of the pancreas and may account for up to 60% of all neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas. Ninety percent of nonfunctioning tumors are malignant at presentation. Patients with nonfunctioning tumors do not have any symptoms from excessive hormone secretion by the tumor because the tumor does not release any hormones into the blood.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Clinical Findings
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree