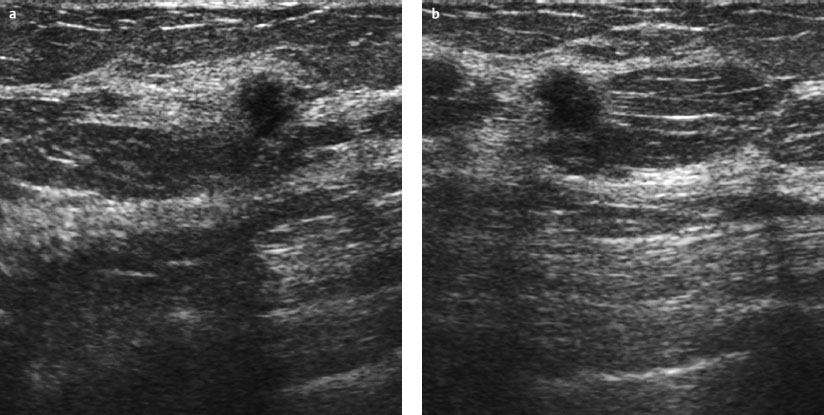
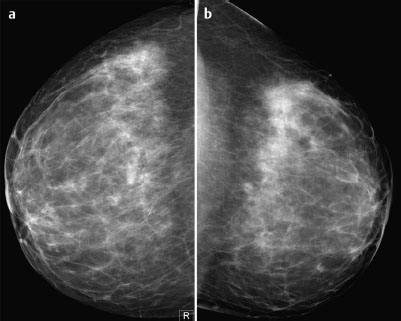
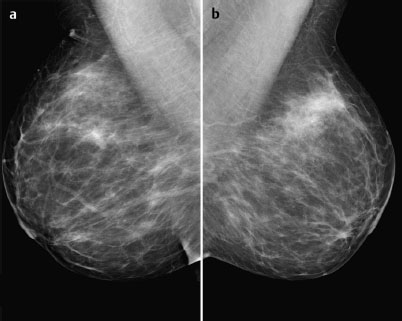
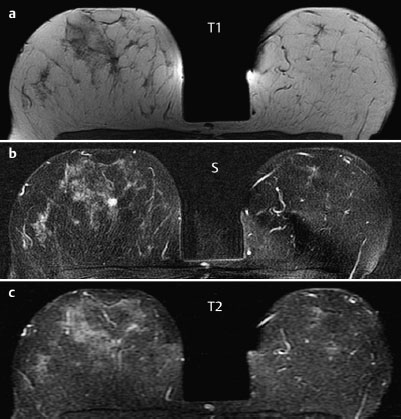
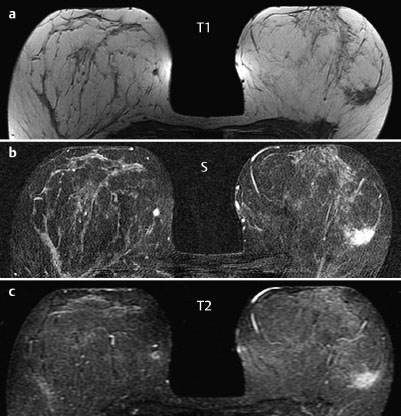
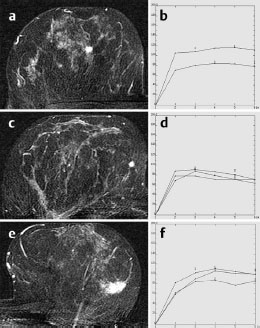
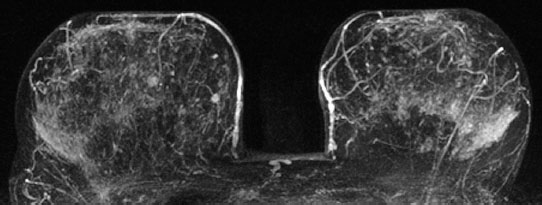
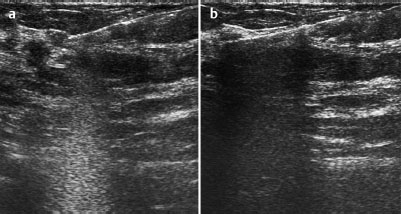
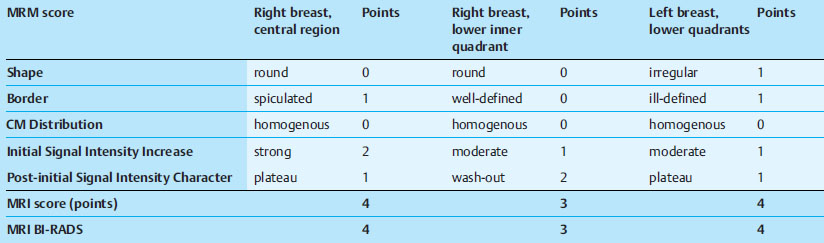
Case 48 Indication: Screening mammography. History: Unremarkable. Risk profile: No increased risk. Age: 64 years. Inspection and palpation unremarkable. Fig. 48.1 a,b Ultrasound images of the central part of the right breast from two angles. Fig. 48.2a,b Digital mammography, CC view. Fig. 48.3a,b Digital mammography, MLO view. Fig. 48.4a-c Contrast-enhanced MRI of the breasts. Fig. 48.5a–c Contrast-enhanced MRI of the breasts. Fig. 48.6a–f Signal-to-time curves. Fig. 48.7 Contrast-enhanced MR mammography. Maximum intensity projection. Please characterize ultrasound, mammography, and MRI findings. What is your preliminary diagnosis? What are your next steps? This case shows the imaging studies of an asymptomatic woman. In the right breast, ultrasound demonstrated a partially lobulated, hypoechoic lesion, measuring 9 mm, with echogenic margins. No architectural distortion. There were no further findings in ultrasound. US BI-RADS right 4/left 1. The parenchyma was bilaterally almost completely symmetric and inhomogeneously dense, ACR type 3. Mammograms showed no suspicious findings. In particular, the area corresponding to the sonographic finding between the upper quadrants of the right breast showed no densities, no architectural distortions, and no calcifications. BI-RADS right 1/left 1. PGMI: CC view P; MLO view G (inframammary fold). Between the upper quadrants of the right breast, MRI depicted a hypervascularized, irregular mass (diameter 1 cm) with intermediate signal in T2-weighted imaging. Initial signal increase was 110%, followed by a postinitial plateau (MRM score 4). Radial spiculations were clearly visible on precontrast images. MRI also showed another hypervascularized lesion measuring 8 mm in the lower inner quadrant of the right breast with centrally reduced and peripherally increased T2 signal. Initial signal increase was90% with postinitial washout (MRM score 3). There was also regional enhancement in the lower outer quadrant of the left breast with an initial signal increase of 100%, postinitial plateau, and increased signal in T2-weighted imaging. MRI Artifact Category: 1 MRI Density Type: 2 Right: Multicentric carcinoma, bifocal fibroadenoma. Left: Adenosis, diffuse carcinoma.
Clinical Findings

Ultrasound
Mammography
MR Mammography
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
BI-RADS Categorization | ||
Clinical Findings | right 1 | left 1 |
Ultrasound | right 4 | left 1 |
Mammography | right 1 | left 1 |
MR Mammography | right 4 (multicentric) | left 4 |
BI-RADS Total | right 4 | left 4 |
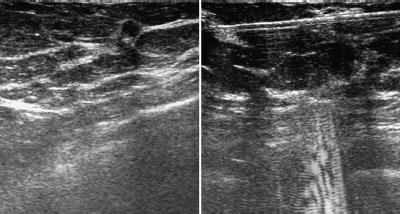
Fig. 48.8 a,b US-guided core biopsy of the central lesion in the right breast. Pre-fire and post-fire documentation.
Fig. 48.9 Ultrasound of the lower inner quadrant of the right breast.
Fig. 48.10 US-guided core biopsy of the second lesion in the rightbreast.
Procedure
Histopathological analysis of the lesion between the upper quadrants of the right breast by US-guided percutaneous core biopsy.
Histopathology of the right breast
Invasive ductal carcinoma between the upper quadrants of the right breast.
What about the second lesion seen in MRI in the right breast?
A targeted sonographic re-examination detected a hypoechoic lesion of diameter 4 mm with echogenic margins. Here US-guided core biopsy was also performed (Figs. 48.9 and 48.10).
Histopathology of the second lesion(lower inner quadrant of right breast)
Invasive ductal carcinoma.
Regional enhancement in the left breast (MRI BI-RADS 4)
Because there were no findings in ultrasound and mammography consistent with this enhancing area, no biopsy was performed here. A follow-up was carried out after 6 months. This follow-up did not reproduce the enhancement in this area.
Histology
Invasive ductal carcinomas of the right breast with a diameter of 8 mm and 7 mm. Lymph node status normal.
IDC (multicentric) pT1 b, pN0, G2
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree