, Joon Woo Lee1 and Jong Won Kwon2
(1)
Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Kyonggi-do, Republic of Korea
(2)
Department of Radiology, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Abstract
Some spinal disorders may be confused with other conditions presenting with similar imaging findings. This can be a cause of misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis. In this chapter, we will present practical tips useful in the differentiation and correct diagnosis of 20 pairs of spinal disorders with similar imaging features.
Some spinal disorders may be confused with other conditions presenting with similar imaging findings. This can be a cause of misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis. In this chapter, we will present practical tips useful in the differentiation and correct diagnosis of 20 pairs of spinal disorders with similar imaging features.
19.1 Introduction
Confusing spinal disorders are not uncommonly encountered in daily routine practice; reliably differentiating between real lesions and mimics, tumors and non-tumoral masses, as well as benign and malignant lesions is often challenging. For example, a herniated disk can mimic an epidural tumor such as a schwannoma, especially if the herniated disk is sequestered away from the parent disk and shows high T2-weighted signal with enhancement. Nonetheless, there are often useful imaging clues that allow for differentiation of these conditions.
In this chapter, we will describe practical tips helpful in the accurate diagnosis of the following potentially confusing spinal disorders: herniated disk versus schwannoma, spondylolytic versus degenerative spondylolisthesis, focal red marrow versus metastasis, postoperative scar versus recurrent disc herniation, benign osteoporotic vertebral fracture versus malignant vertebral fracture, os odontoideum versus odontoid process fracture, neurofibromatosis type 1 versus type 2, infectious spondylitis versus Modic type 1 endplate degenerative change, spinal cord herniation versus intradural arachnoid cyst, spinal arteriovenous fistula versus hypervascular tumor with intratumoral shunt, ankylosing spondylitis versus diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis, pyogenic spondylitis versus tuberculous spondylitis, spinal cord tumor versus nonneoplastic myelopathy, acute transverse myelitis versus multiple sclerosis, ependymoma versus astrocytoma, schwannoma versus meningioma, chordoma versus giant cell tumor, vertebral hemangioma versus Paget’s disease, sacroiliitis of spondyloarthropathy versus osteitis condensans ilii, as well as sacral insufficiency fracture versus sacral osteomyelitis.
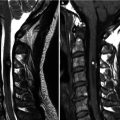
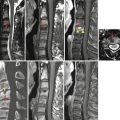
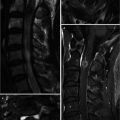
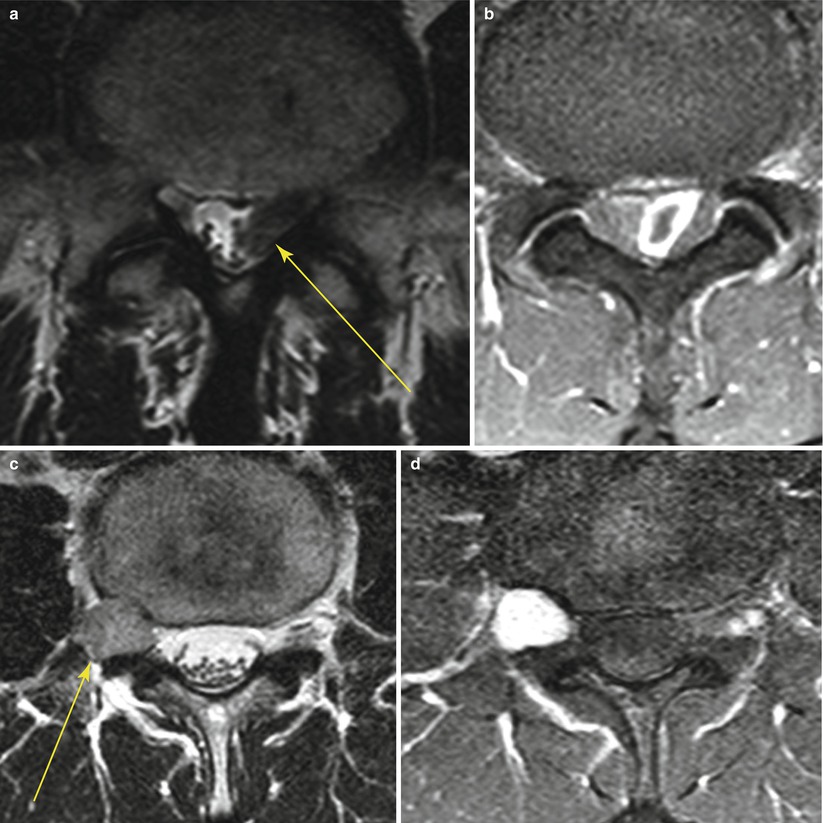
19.2 Herniated Disk (Sequestration) Versus Schwannoma
Similarities | Epidural mass | |
Can be similar signal on T2-weighted image (high or low signal in both) | ||
Can be enhanced | ||
Differences | Peripheral enhancement (with inner T2-low-signal area) | Homogeneous enhancement |
Inner low signal on T2-weighted image (common) | Peripheral enhancement (with inner T2-high signal) | |
Radial tear or protrusion in the near side of parent intervertebral disk | High signal on T2-weighted image (common) | |
Dumbbell shape, bone erosion | ||
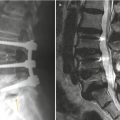
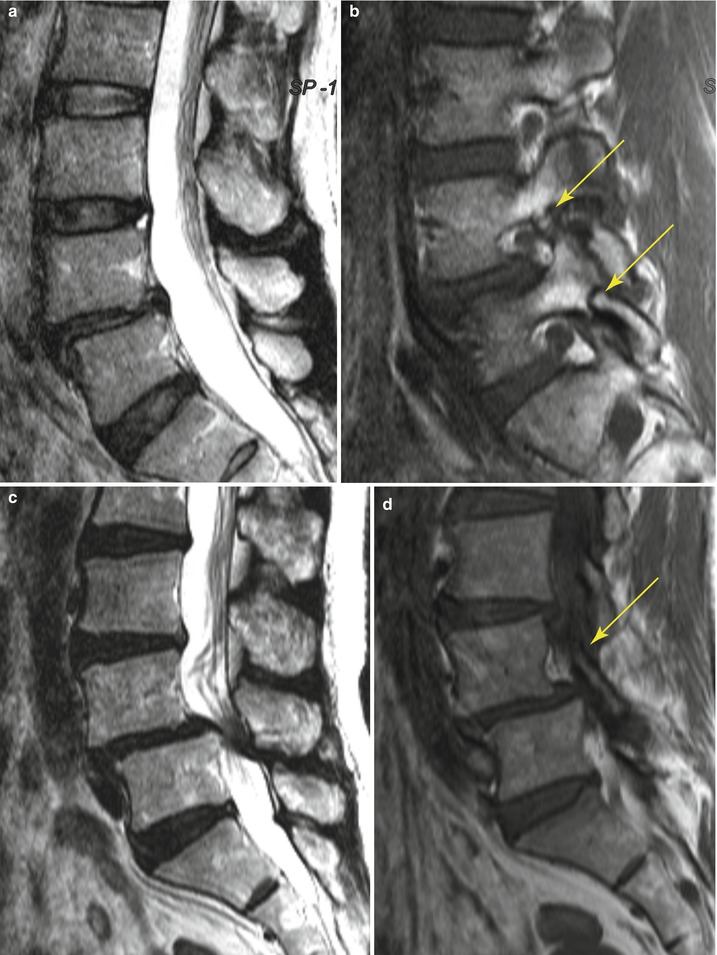
19.3 Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis Versus Degenerative Spondylolisthesis
Similarities | Anterior displacement of vertebral body compared with vertebral body below | |
Foraminal stenosis | ||
Differences | Central canal widening | Central canal narrowing |
Non-displaced spinous process | Anteriorly displaced spinous process | |
Defect pars interarticularis | Intact pars interarticularis | |
Most common in L5–S1 | Most common in L4–5 | |
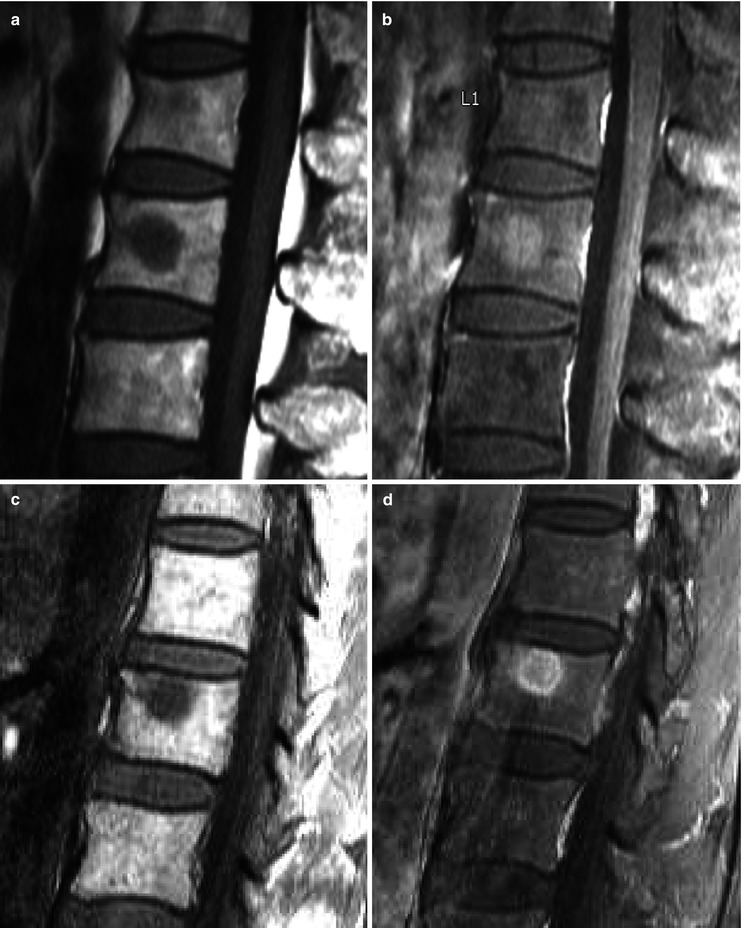
19.4 Focal Red Marrow Versus Metastasis
Similarities | Focal nodule | |
Lower signal on T1-weighted image than that of surrounding fatty marrow | ||
Enhancement | ||
Differences | Isointense or slightly hyperintense to the intervertebral disk on T1-weighted images | Hypointense to the intervertebral disk on T1-weighted images |
Bright central area on T1-weighted images | No central fatty area | |
Patchy enhancement | Strong enhancement | |
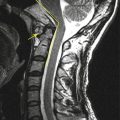
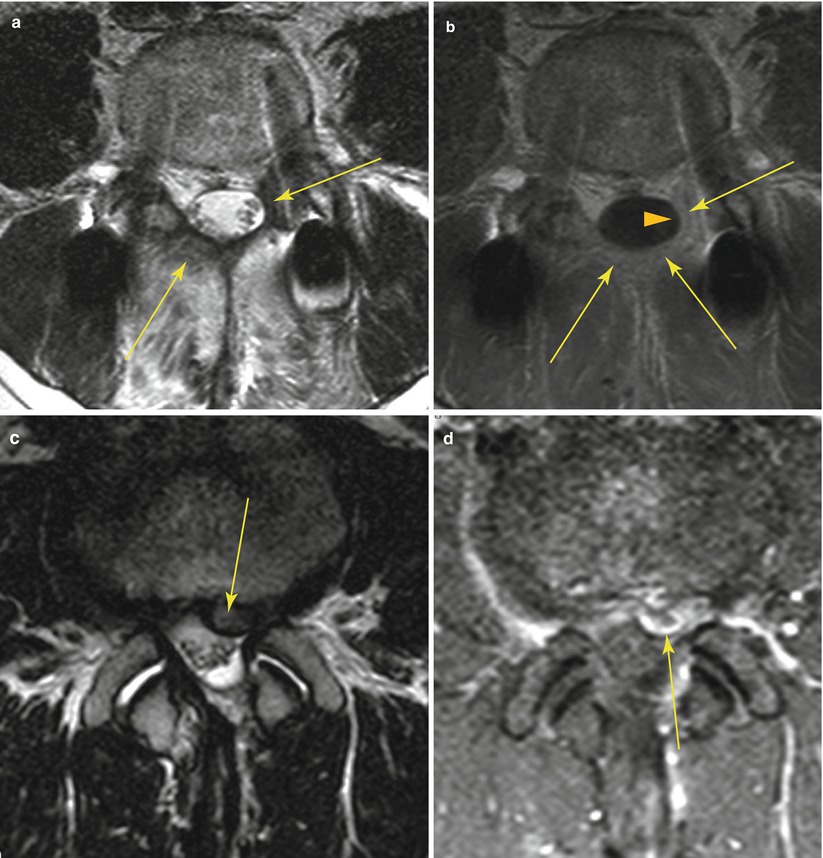
19.5 Postoperative Scar Versus Recurrent Disk Herniation
Similarities | Space occupying lesion in the epidural space | |
Differences | Retraction of adjacent structures | Displaces or compresses adjacent structures |
Homogeneous enhancement | Peripheral or no enhancement | |
Ill-defined margins | Well-defined margins | |
Discontinuity from the parent disk | Continuity with the parent disk | |
19.6 Benign Vertebral Fracture Versus Malignant Vertebral Fracture
Similarities | Vertebral compression or burst fracture without history of trauma or with minimal trauma | |
Differences | Preservation of normal bone marrow signal in the fractured vertebra | Bone marrow signal change involving the whole vertebral body |
Mild low signal change in the vertebral body on T1-weighted images | Marked low T1 signal change in the vertebral body on T1-weighted images | |
Less intense bone marrow enhancement
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

| ||