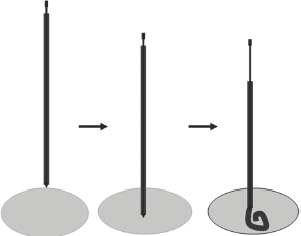
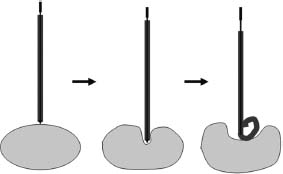
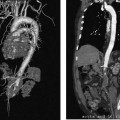
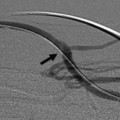
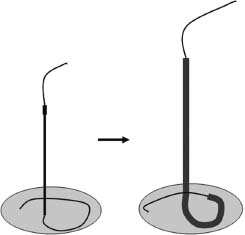
CASE 50 An 18-year-old male presented to us after appendectomy for appendicitis. At surgery, the patient was found to have Crohn’s disease involving the terminal ileum. Five days after surgery, the patient complained of increasing abdominal pain associated with fever and leukocytosis. Figure 50-1 An 18-year-old male presented with Crohn’s disease after appendectomy with increasing abdominal pain, fever, and leukocytosis. (A) CT scan shows a large fluid collection with air bubbles in the pelvis. (B) and (C) CT at follow-up 3 days later showed near complete resolution of the collection. The drainage catheter was in place. CT scan showed a large pelvic fluid collection containing air bubbles (Fig. 50-1A). We discuss treatment options and how to perform percutaneous drainage. Pelvic abscess. Figure 50-2 Seldinger technique. The abscess is punctured with a needle, and using a wire, the catheter is introduced over the wire after dilatation of the tract. If a micropuncture system is used initially, exchange to a working 0.035-inch wire through transitional dilators is required. Percutaneous drainage catheter placement was performed under ultrasound guidance and an 8-French (F) catheter was placed into the fluid collection. Follow-up CT performed 5 days later showed near resolution of the fluid collection (Figs. 50-1B, C). The catheter was removed, and the patient had an uneventful recovery. Drainage catheter Puncture needle Wire Access was made using the Seldinger technique (Fig. 50-2). When a micropuncture system is used, the micropuncture needle is used to access the fluid collection under imaging guidance. The transitional wire is then passed through the needle, and a coaxial dilator system is introduced over the wire. The inner dilator and wire are removed, and a working 0.035-inch wire is introduced through the outer dilator. If using a “one stick” needle, a needle large enough to accept a 0.035-inch wire is used. Once the needle enters the fluid collection, a 0.035-inch wire is passed through the hollow needle. The tract is dilated with up to or one French size larger than the catheter size. The drainage catheter is placed into the fluid collection over a wire. The wire is removed, and the pigtail loop of the catheter is locked. The catheter can be put to gravity drainage if the fluid collection is large or to bulb suction. Figure 50-3 Trocar technique. Illustration depicts the entire catheter-needle set advanced into the fluid collection. The catheter is advanced forward to form the pigtail loop. Figure 50-4
Clinical Presentation
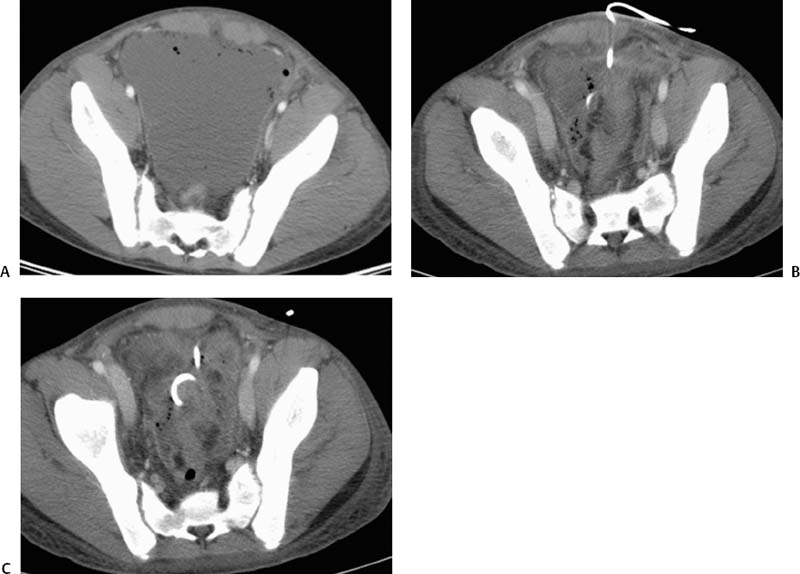
Radiologic Studies
Diagnosis
Treatment
Equipment
Seldinger Technique
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree