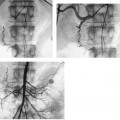
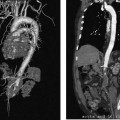
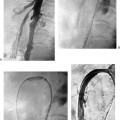
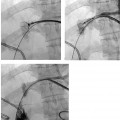
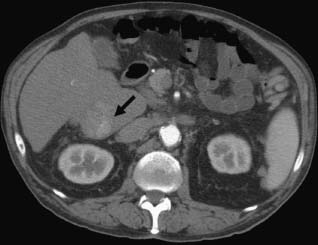
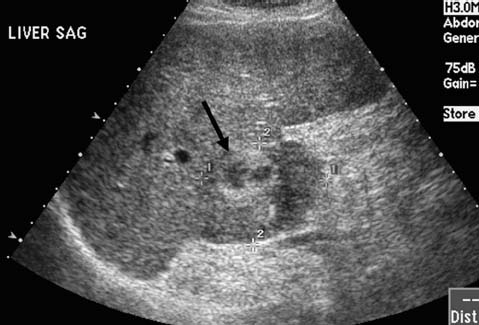
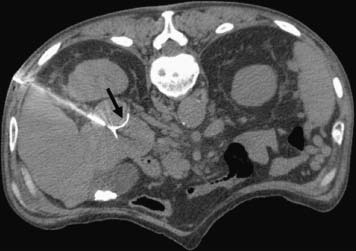
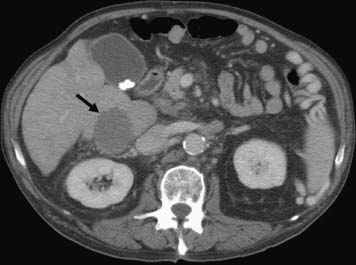
CASE 52 A 64-year-old male with a history of squamous cell carcinoma at the base of the tongue and alcoholic cirrhosis underwent routine surveillance abdomen CT. The squamous cell cancer had been treated with resection and chemotherapy 5 years earlier. The patient had been disease-free in the interval. Figure 52-1 Contrast-enhanced CT shows an enhancing mass in the caudate lobe of the liver (arrow). CT scans showed the liver with a nodular contour. There was a 3-cm hypervascular mass in the caudate lobe of the liver (Fig. 52-1). Ultrasound examination showed a heterogeneous mass in the caudate lobe of the liver (Fig. 52-2). The patient underwent ultrasound-guided percutaneous biopsy of the liver lesion. Pathology was consistent with a well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Well-differentiated HCC. The patient underwent radiofrequency ablation (RFA). The patient was placed prone on the CT gurney. General endotracheal anesthesia was provided by the anesthesiology department. Under CT guidance, a LeVeen coaxial radiofrequency (RF) needle (RadioTherapeutics, Boston Scientific, Natick, Massachusetts) was advanced into the tumor, and the tines were deployed. RFA was performed until roll-off was achieved. Overlapping areas were ablated (Fig. 52-3). Figure 52-2 Ultrasound shows a heterogenous lesion in the caudate lobe of the liver (arrow). Figure 52-3 CT performed during RFA probe placement shows the probe tip with its fully deployed tines (arrow) in the region of the tumor. Figure 52-4 Follow-up contrast-enhanced CT shows a hypodense area without enhancement to suggest residual tumor or recurrence. The patient had a follow-up CT 8 weeks after ablation, which showed a hypodense area in the ablated region. There was no evidence of enhancement in the area of the treated tumor to suggest residual or recurrent tumor. Further follow-up in 3 months showed a smaller hypodense lesion in the same location without enhancement (Fig. 52-4). Three types of RFA probes are currently commercially available. Generators for these probes are different as are the generator algorithms. The LeVeen needle (RadioTherapeutics, Boston Scientific, Natick, Massachusetts) electrode has retractable curved electrodes and comes in various sizes up to 5 cm. When fully deployed, the electrodes assume an umbrella shape. The algorithm is based on a slow rise in power to avoid charring. Impedance in the tissue is measured until there is a rapid rise in impedance as the tissue desiccates. “Roll-off” or rapid rise in impedance is believed to indicate successful ablation. The time for ablation is typically 20 to 30 minutes per ablation, which consist of two cycles. The RITA probe (RITA Medical Systems, Mountain View, California) also has electrodes that are deployed once the needle tip is in position. The temperatures of the electrodes are monitored and the target temperature is maintained for 8 to 12 minutes through regulation of the power output by the generator.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Studies
Diagnostic Procedure
Diagnosis
Treatment
Equipment
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree