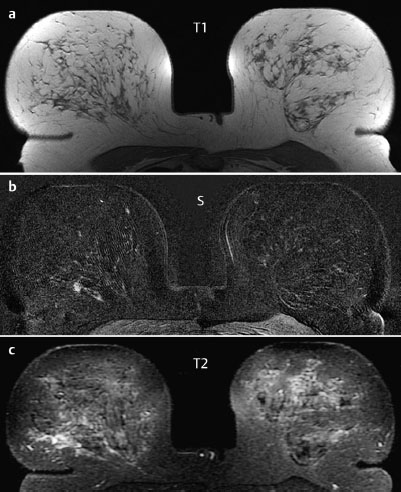
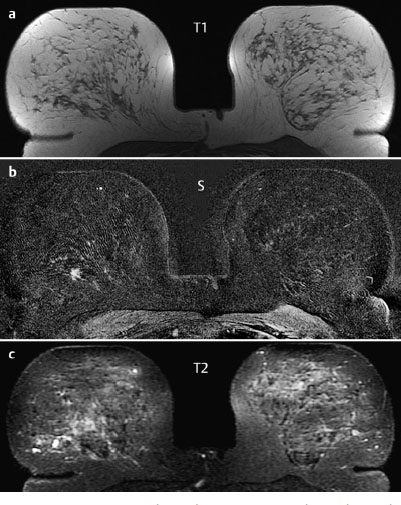
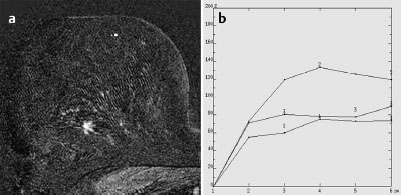
MRM score | Finding | Points |
Shape | irregular | 1 |
Border | spiculated | 1 |
CM Distribution | homogenous | 0 |
Initial Signal Intensity Increase | strong | 2 |
Post-initial Signal Intensity Character | plateau | 1 |
MRI score (points) |
| 5 |
MRI BI-RADS |
| 4 |
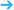 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
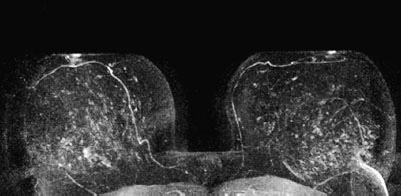
Focal adenosis, radial scar, carcinoma (tubular?).
Clinical Findings | right 1 | left 1 |
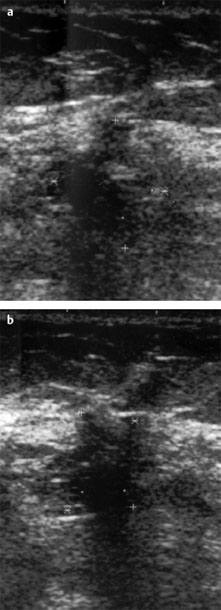
Ultrasound | right 3 | left 1 |
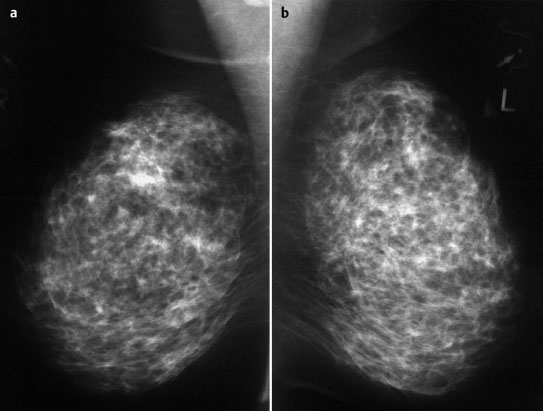
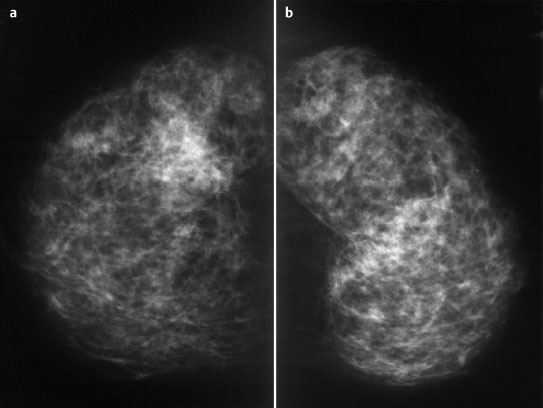
Mammography | right 1 | left 1 |
MR Mammography | right 4 | left 1 |
BI-RADS Total | right 4 | left 1 |
Procedure
MR-guided vacuum biopsy. A US-guided biopsy could also be considered as an alternative. In the latter case, the correspondence between US and MRI findings must be very firmly established.
Histology
Invasive lobular carcinoma.
Fig. 55.8a–d MR-guided vacuum biopsy.
a Subtraction image reproducing the suspicious finding.
b Documentation of coaxial needle.
c Area of resection after biopsy.
d Final documentation following further contrast administration, showing enhancement due to bleeding.
Histology
Diffuse invasive lobular carcinoma.
ILCpT2pN0, G1.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree