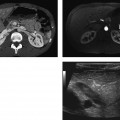
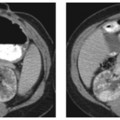
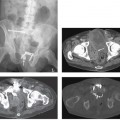
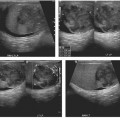
CASE 55 A 21-year-old patient presents with recurrent urinary tract infections. Contrast-enhanced axial computed tomography (CT) images demonstrate an atrophic right kidney (Fig. 55.1A) with renal cortical scarring and dilatation of the right renal pelvis. Sequential images from a voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG) demonstrate contrast opacification of the urinary bladder, the right ureter, and the right renal collecting system (Fig. 55.1B). There is dilatation of the right renal pelvis and ballooning of the renal calyces. Atrophic right kidney secondary to reflux nephropathy Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) is defined as the retrograde flow of urine from the urinary bladder toward the kidney. Although VUR is classically described as a disorder affecting children, structural changes within the kidney are often detected in adulthood. The most common clinical presentation of VUR is urinary tract infection.
Clinical History
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Clinical Findings
Complications
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree