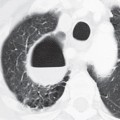
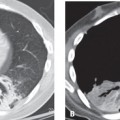
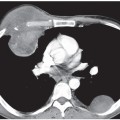
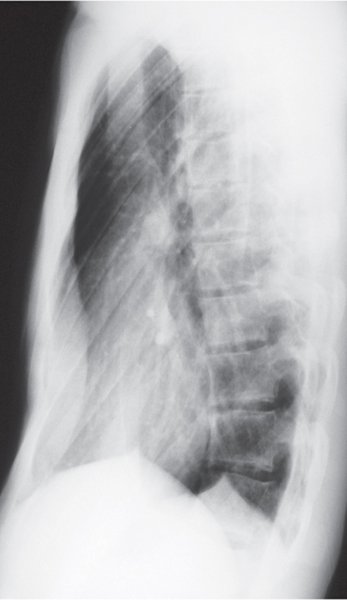
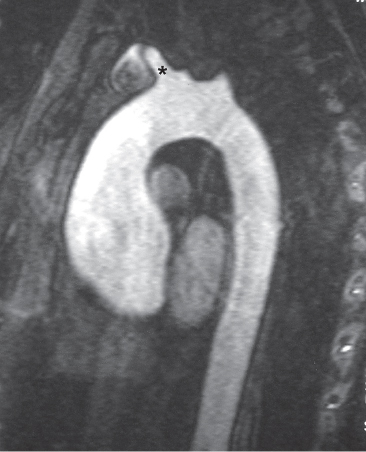
CASE 6 18-year-old man with recurrent pneumothorax PA (Fig. 6.1) and lateral (Fig. 6.2) chest radiographs demonstrate a right pneumothorax and thickening of the right apical pleura (Fig. 6.1). Note the abnormal cardiac contour, enlargement of the pulmonary trunk, and pectus excavatum deformity (Figs. 6.1, 6.2). Note left apical pleural thickening and metallic sutures (Fig. 6.2) (arrow) from previous lung resection for treatment of recurrent pneumothorax. Oblique sagittal gradient-echo MRA (Fig. 6.3) shows dilatation of the proximal ascending aorta and sinuses of Valsalva. Marfan Syndrome Fig. 6.1 Fig. 6.2 Fig. 6.3 • Primary Spontaneous Pneumothorax • Annuloaortic Ectasia of Other Etiology (Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, Turner Syndrome, Polycystic Kidney Disease, Osteogenesis Imperfecta) • Aortic Stenosis with Post-Stenotic Dilatation • Aortic Dissection Marfan syndrome is a systemic connective tissue disorder involving primarily elastic tissues that affects the central nervous system, eye, skeleton, lung, and cardiovascular structures. Marfan syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder, but may occur sporadically in up to 30% of cases.
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Radiologic Findings
Radiologic Findings
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis

 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
 Discussion
Discussion
Background
Etiology
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Radiology Key
Fastest Radiology Insight Engine