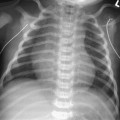
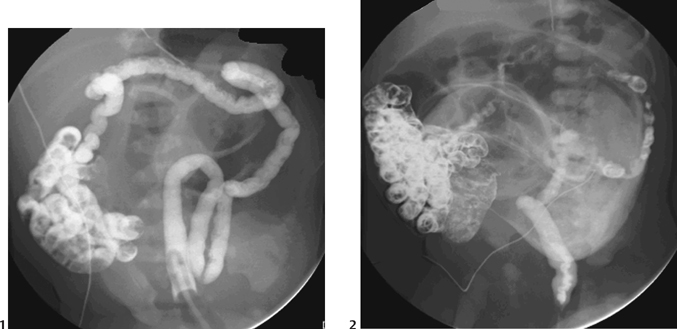
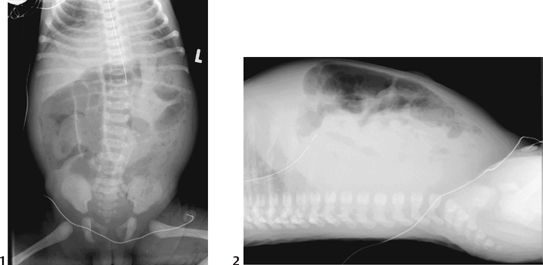
CASE 60 Term neonate presents with a distended abdomen and failure to pass meconium after 48 hours. Figure 60A Non-ionic contrast enema (Fig. 60A1) in a 2-day-old girl demonstrates a microcolon. Reflux of contrast has occurred into mildly dilated loops of distal ileum, containing meconium plugs, but does not reach the more proximal dilated air-filled loops. Further reflux was achieved during a repeat examination the following day (Fig. 60A2), with opacification of significantly more dilated loops in the mid-ileum, containing further inspissated meconium. Meconium ileus Meconium ileus is a neonatal obstruction of the ileum by abnormally viscid, inspissated pellets of meconium. Low GI obstruction—abdominal distension, failure to pass meconium, and sometimes vomiting — within the first 48 hours of life Figure 60B Supine (1) and cross-table lateral (2) abdominal x-ray of a 2-day-old girl showing generalized bowel dilatation with a mottled appearance of air mixed with meconium, in this case more prominent in the left flank. Enema confirmed meconium ileus with an underlying diagnosis of CF.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Etiology
Clinical Findings
Associated Conditions
Complications
Pathology
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree