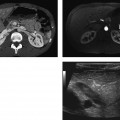
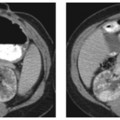
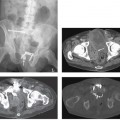
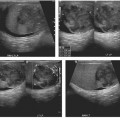
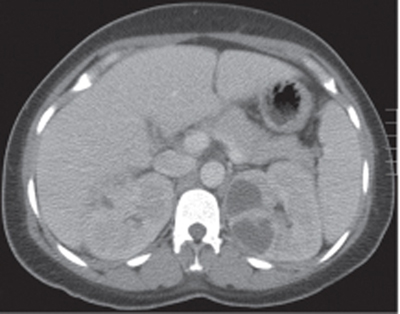
CASE 65 A 78-year-old diabetic man presents with a spiking fever and flank pain. Fig. 65.1 Axial contrast-enhanced CT image in a diabetic patient with a history of urinary tract infection shows an ill-defined, hypodense corticomedullary renal abscess. Axial contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) image shows an ill-defined, hypodense left renal lesion with thick walls (Fig. 65.1). Renal abscess A renal abscess is an uncommon renal condition. It can be cortical or corticomedullary, depending on the route of infection. When left untreated, a renal abscess can lead to significant mortality and morbidity. With the use of image-guided intervention techniques and antibiotics, mortality and morbidity due to renal abscess are significantly reduced.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Clinical Findings
Complications
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree