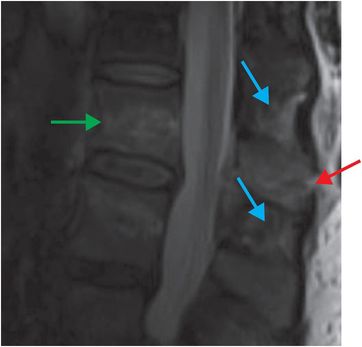
Diagnosis: Flexion distraction injury at L1
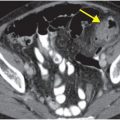
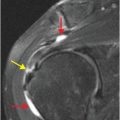
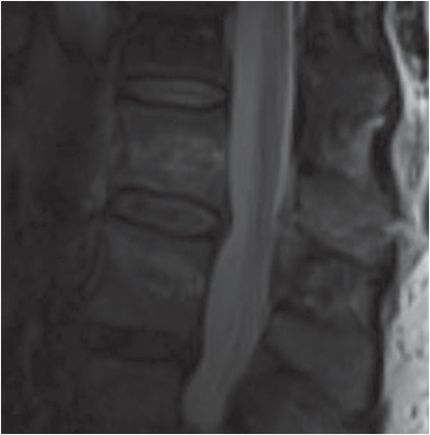
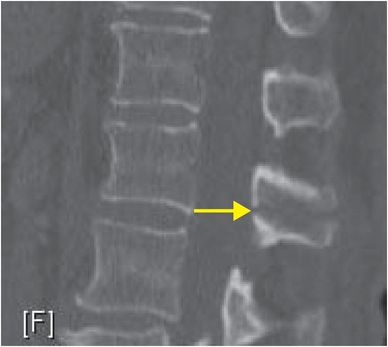
Sagittal CT of the thoracolumbar spine demonstrates a transversely oriented fracture through the spinous process of L1 (yellow arrow). No other fractures are evident. Mechanism of injury (restrained motor vehicle accident) and fracture pattern raised concern for flexion distraction injury; thus, MRI was performed. Sagittal STIR MRI of the lumbar spine demonstrates disruption of the supraspinous ligament at the spinous process of L1 (red arrow), edema within the interspinous ligaments (blue arrows), and fracture of the L1 vertebral body (green arrow).
Discussion
In thoracic and lumbar trauma, the thoracolumbar junction is the most common site of injury – more than 50% of injuries occur between T11 and L1.
In the upright position, the center of gravity of the human body is immediately anterior to the thoracolumbar spine. At rest, there are compressive forces on the vertebral bodies and distractive forces on the posterior ligamentous structures.
The posterior ligamentous complex (PLC), consisting of the supraspinous ligament, interspinous ligaments, articular facet capsules, and ligamentum flavum, plays a key role in maintaining spinal stability when there is injury to the vertebral bodies.
Injury to the PLC usually requires surgical correction to prevent kyphotic progression with vertebral body collapse.
Thoracolumbar injuries can be scored and classified according to the thoracolumbar injury classification and severity score (TLICS), which was developed by the Spine Trauma Study Group.
Scoring requires assessment of three parameters: injury morphology, integrity of the PLC, and neurological status. This classification system assesses biomechanical and neurological spinal stability, and influences management decisions.
A useful framework for understanding spinal injury divides the spine into anterior, middle, and posterior compartments (see “Flexion teardrop fracture” case for further explanation).
| Injury category | Point value |
|---|---|
| Injury morphology | |
| Compression | 1 |
| Burst | 2 |
| Translation or rotation | 3 |
| Distraction | 4 |
| PLC status | |
| Intact | 0 |
| Injury suspected | 2 |
| Injured | 3 |
| Neurologic status | |
| Intact | 0 |
| Nerve root involvement | 2 |
| Spinal cord or conus injury, complete | 2 |
| Spinal cord or conus injury, incomplete | 3 |
| Cauda equina syndrome | 3 |
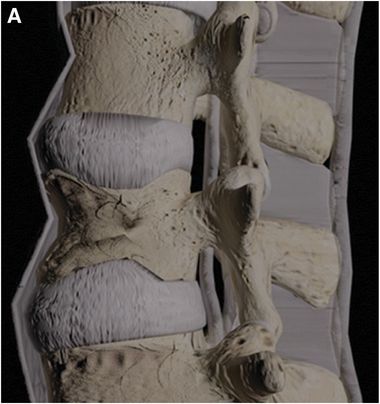
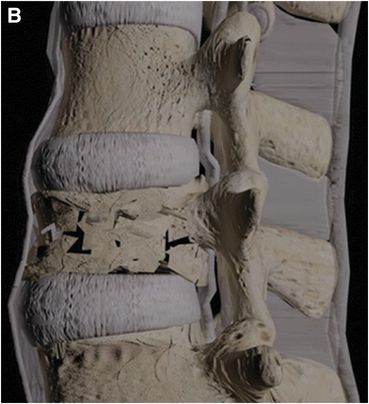
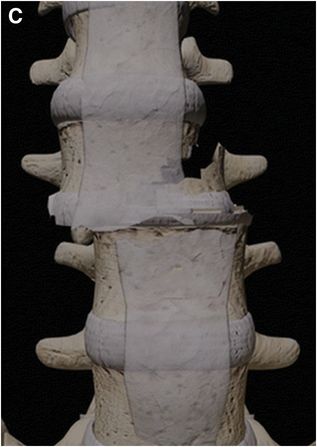
Computer-generated graphic of thoracolumbar fracture injury morphology with TLICS scoring: A: Compression (1 point). B: Compression with burst fracture (2 points). C: Translation or rotation (3 points). D: Distraction (4 points).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree