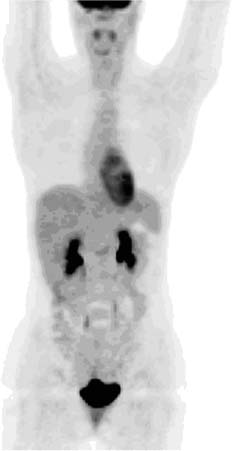
CASE 68 A 35-year-old woman is referred for PET with 2-deoxy-2-[18F-FDG]. Fig.68.1 PET scan with 18F-FDG. • The patient is instructed to avoid vigorous exercise for 24 hours prior to the scan, fast for at least 4 hours before the study, drink water during the fasting and uptake periods, and void prior to the scan • A venous serum glucose sample is obtained prior to the injection of 18F-FDG (reference range is < 120 mg/dl for non-diabetic patients and < 200 mg/dl for diabetic patients), and the patient’s height and weight are recorded • A 10–20 mCi dose of 18F-FDG is injected intravenously (in a dimly lit quiet room for brain PET scans), and the patient is asked to rest comfortably in a room that is kept warm • Most PET scans are now acquired on a hybrid PET/CT scanner, and a low dose spiral CT is acquired for attenuation correction of the PET images and for anatomic localization. Some centers may choose to perform oral and/or intravenous contrast-enhanced diagnostic CT as part of the PET/CT examination • Sixty minutes following the 18F-FDG injection, the spiral CT is performed using a weight-based algorithm from the skull base to the upper thighs (for most oncologic indications), or from the vertex to the feet, or centered over the brain depending on the tumor being evaluated • Consistency in 18F-FDG injected dose, scan acquisition time relative to the injection time, and acquisition and reconstruction protocols is important when performing serial scanning on the same patient Anterior view from the three-dimensional maximum-intensity pixel (MIP) image (Fig. 68.1) demonstrates intense 18F-FDG uptake in the brain, heart, renal collecting systems, ureters, and bladder. There is more moderate uptake in the liver, spleen, colon, and various mucosal structures of the head and neck, as well as mild uptake in the thyroid, mediastinal blood pool, bone marrow, and skeletal muscles. Normal 18F-FDG-PET scan. Normal 18F-FDG-PET scan. Diagnosis final, no clinical follow-up. This case reflects the typical normal findings in an 18
Clinical Presentation
Technique
Image Interpretation
Differential Diagnosis
Diagnosis and Clinical Follow-Up
Discussion
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree