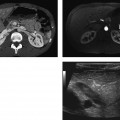
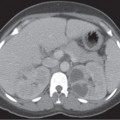
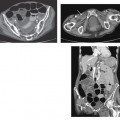
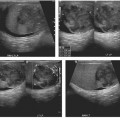
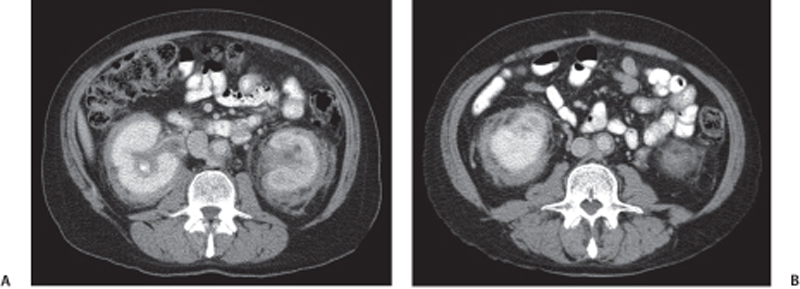
CASE 69 A 65-year-old man complains of a dull back pain. Fig. 69.1 (A,B) Axial contrast-enhanced CT images show diffuse bilateral soft tissue infiltration of the perirenal space extending into the renal hilum with evidence of hydronephrosis. There is also plaquelike thickening surrounding the aorta and the medial aspect of the inferior vena cava. Axial contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) images show diffuse bilateral soft tissue infiltration of the perirenal space extending into the renal hilum with evidence of hydronephrosis. There is also plaquelike thickening surrounding the aorta and the medial aspect of the inferior vena cava (IVC) (Fig. 69.1). Retroperitoneal fibrosis (RPF) RPF is a relatively uncommon clinical entity, predominantly affecting men in their 4th to 6th decade. This disorder is characterized by the development of extensive fibrosis occurring throughout the retroperitoneum, ultimately leading to encasement and entrapment of retroperitoneal structures. RPF usually begins at the level of the fourth and fifth lumbar vertebrae and subsequently spreads cephalad, encasing the aorta, IVC, and ureters.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Clinical Findings
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree