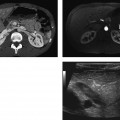
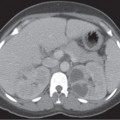
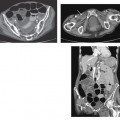
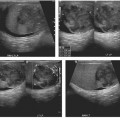
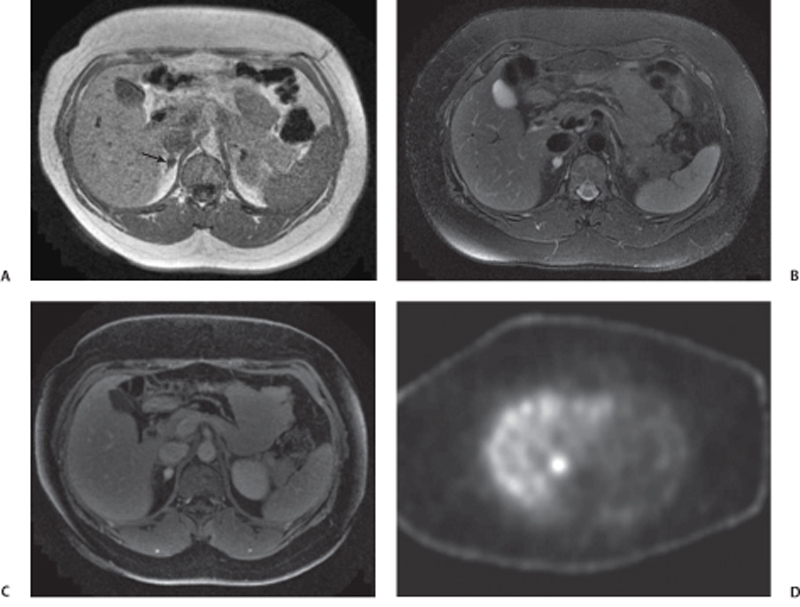
CASE 72 A 41-year-old woman presents with a history of persistent hypertension. Fig. 72.1 (A) Axial T1-weighted image shows a well-defined right adrenal nodule (arrow) isointense to muscle. (B) Axial T2-weighted image shows the lesion to have homogeneous high signal intensity. (C) Axial postcontrast image shows homogeneous enhancement within the lesion. (D) I 123 MIBG SPECT scan shows a high uptake in the right adrenal region. Magnetic resonance (MR) images of the right adrenal gland show a small hypointense lesion on the T1-weighted sequence that is hyperintense on the T2-weighted image and shows homogeneous intense enhancement on the postcontrast image. The lesion is uniformly hot on I 123 thyroid, MIBG (iobenguane/m-iodobenzylguanidine) single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) scan (Fig. 72.1). Pheochromocytoma Paraganglioma, when present in the adrenal medullary location, is referred to as pheochromocytoma. When extra-adrenal, these tumors have more malignant potential and are commonly referred to as paragangliomas or chemodectomas. The most common extra-adrenal sites of paragangliomas are the organ of Zuckerkandl (which is the confluence of neural tissue just below the aortic bifurcation), sympathetic chain, and urinary bladder. Pheochromocytoma usually follows the rule of 10 (10% incidence of being extra-adrenal, malignant, bilateral, familial, and not associated with hypertension). Pheochromocytomas are also associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) types 2A and B, von Hippel-Lindau disease, neurofibromatosis 1, cerebellar hemangioblastoma, Sturge-Weber syndrome, tuberous sclerosis, Carney triad, and familial pheochromocytoma.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree