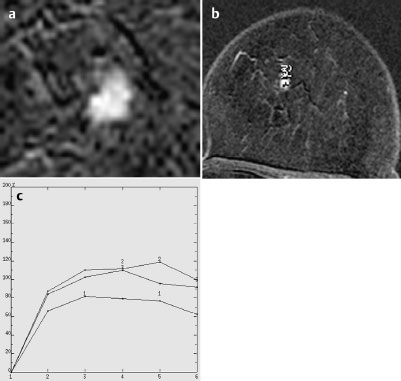
MRM score | Finding | Points |
Shape | irregular | 1 |
Border | ill-defined | 1 |
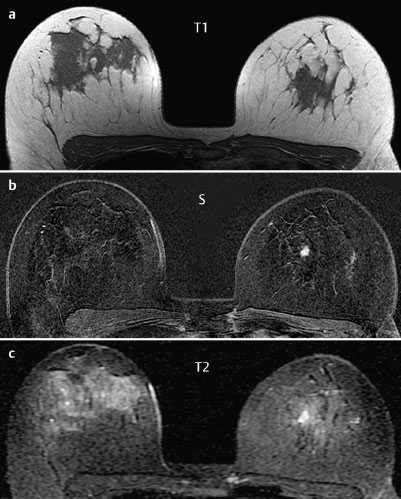
CM Distribution | inhomogeneous | 1 |
Initial Signal Intensity Increase | strong | 2 |
Post-initial Signal Intensity Character | plateau | 1 |
MRI score (points) |
| 6 |
MRI BI-RADS |
| 5 |
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Carcinoma, focal adenosis, papilloma, adenoma.
BI-RADS Categorization | ||
Clinical Findings | right 1 | left 1 |
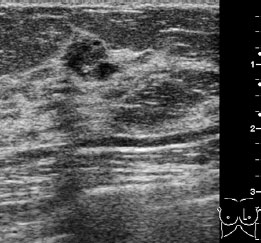
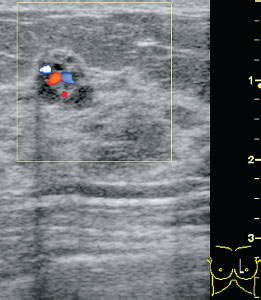
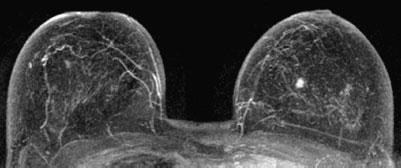
Ultrasound | right 1 | left 4 |
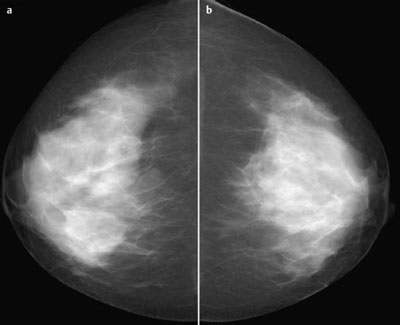
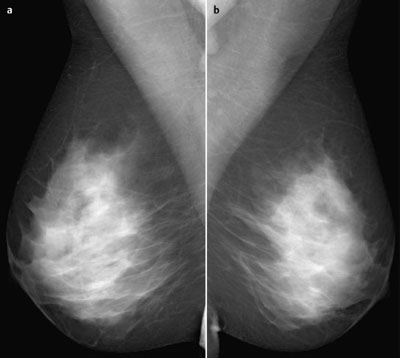
Mammography | right 1 | left 1 |
MR Mammography | right 1 | left 5 |
BI-RADS Total | right 1 | left 5 |
Procedure
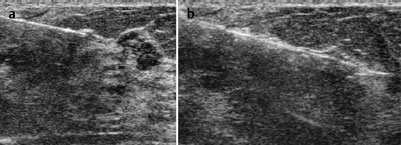
Histopathological investigation with US-guided core biopsy (Fig. 73.8).
Histopathology
Fibrocystic mastopathy. Ductal hyperplasia. Focal apocrine metaplasia. No malignancy.
Procedure
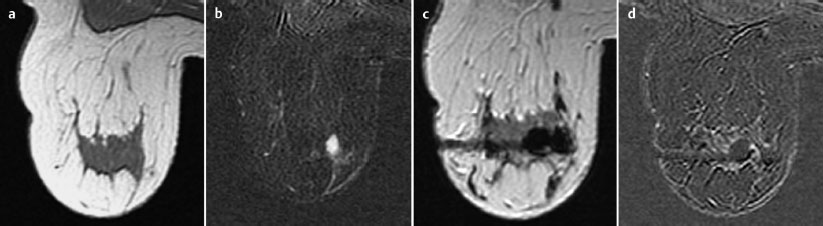
With regard to the possibility of an inaccurate biopsy (sampling error), an additional biopsy was performed, this time an MR-guided vacuum biopsy, for further histological analysis (Fig. 73.9).
Histopathology
Fibrocystic mastopathy. Sclerosing adenosis with ductal and lobular hyperplasia. No malignancy. (Histopathological double reading.)
Fig. 73.8a,b US-guided core biopsy (pre-fire, post-fire)
Fig. 73.9a–d MR-guided vacuum biopsy (precontrast, subtraction after contrast administration, T1-weighted image after biopsy, and documentation of complete removal of the lesion after further contrast administration.
Histology
Tumorous sclerosing adenosis.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree