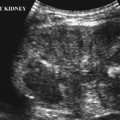
CASE 77 A 6-year-old boy underwent abdominal ultrasonography because of a recent urinary tract infection (UTI). A positive family history of renal disease was present. Figure 77A A longitudinal ultrasound image of the right kidney shows two anechoic lesions, both approximately 1.5 cm in diameter, with some posterior acoustic enhancement typical of renal cysts (Fig. 77A), which corresponded to the family history. The remaining right kidney and the left kidney were normal. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)
Clinical Presentation
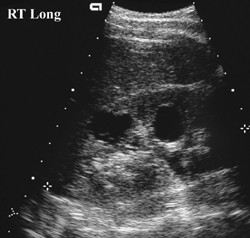
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree