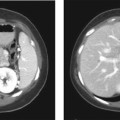
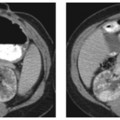
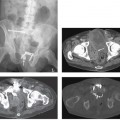
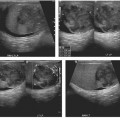
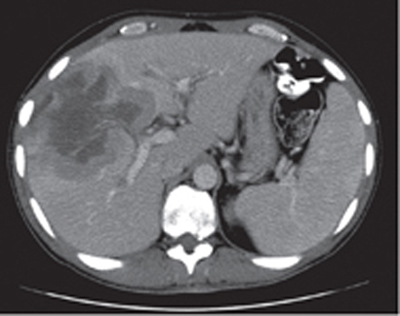
CASE 8 A 57-year-old man presents with abdominal pain, anorexia, and weight loss. Fig. 8.1 Axial contrast-enhanced CT scan show a large, lobulated, hypodense lesion centered in the right lobe of the liver with heterogeneous enhancement. There is no biliary dilatation. No calcification or internal septa are noticed within the lesion. An axial contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) image (Fig. 8.1) shows within the right lobe of the liver a large, hypodense markedly lobulated lesion with a mildly enhancing peripheral wall; the surrounding liver parenchyma appears slightly hypodense probably due to the presence of edema. There is no vessel displacement or biliary tree dilatation. Hepatic lymphoma Secondary hepatic involvement is often described in patients affected by non-Hodgkin and Hodgkin lymphoma, whereas a primary liver lymphoma is a very rare malignancy that has been increasingly reported in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. The most common histology of these lesions is non-Hodgkin B cell lymphoma, usually the diffuse large cell type.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Clinical Findings
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree