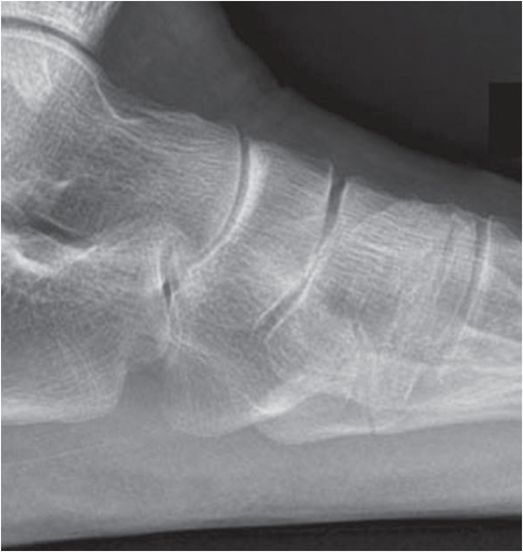
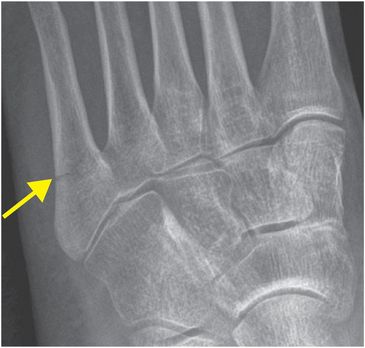
Diagnosis: Acute proximal fifth metatarsal fracture
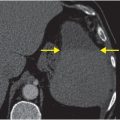
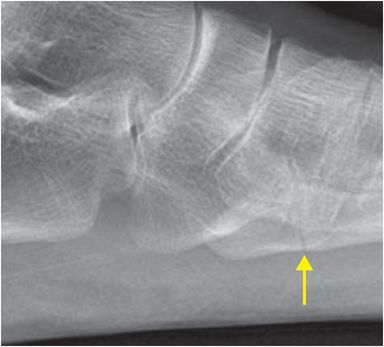
Frontal and lateral radiographs of the left foot demonstrate a transversely orientated, non-displaced, acute extra-articular fracture of the proximal fifth metatarsal (zone 2; arrows).
Discussion
Overview of fifth metatarsal fractures
There are three types of proximal fifth metatarsal fractures, which are classified anatomically into zones. Zone 1 and 2 fractures tend to be caused by trauma, while Zone 3 fractures are seen in the setting of stress fracture.
Zone 1 fracture, also known as an avulsion fracture, is the most proximal fracture type.
Zone 2 fracture, commonly known as a Jones fracture, occurs at the fifth metatarsal metaphyseal–diaphyseal junction. Strictly speaking, a Jones fracture refers to a fracture at the metaphyseal–diaphyseal junction without intra-articular extension to the articulation of the fourth and fifth metatarsals; however, in common usage, the term “Zone 2 fracture” is often used synonymously with “Jones fracture”.
Zone 3 fracture is a diaphyseal fracture, typically occuring as a stress injury.
Anatomy at the base of the fifth metatarsal
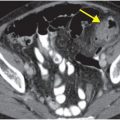
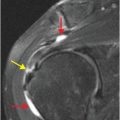
The peroneus brevis tendon attaches at the lateral base of the fifth metatarsal.
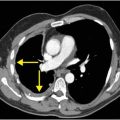
The lateral aspect of the plantar aponeurosis attaches slightly more proximally at the plantar base of the fifth metatarsal.
Avulsion fractures at the base of the fifth metatarsal are thought to be due to combined forces of the peroneus brevis tendon and lateral aspect of the plantar aponeurosis.
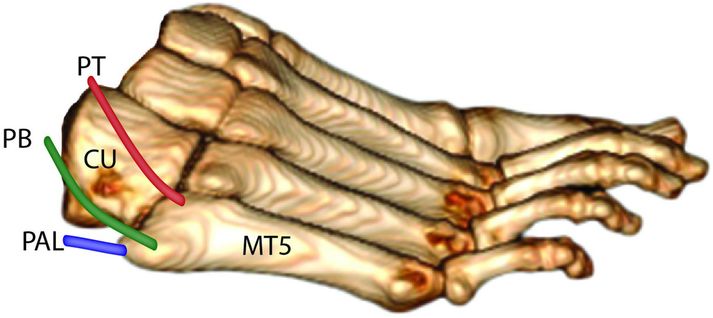
Illustration demonstrates the anatomy at the base of the fifth metatarsal. The peroneus brevis tendon (PB) attaches to the lateral base of the fifth metatarsal (MT5). The lateral aspect of the plantar aponeurosis (PAL) attaches to the plantar base of the fifth metatarsal. The peroneus tertius (PT) tendon attaches dorsally. The cuboid (CU) articulates with the base of the fifth metatarsal to form the fifth tarsometatarsal joint.
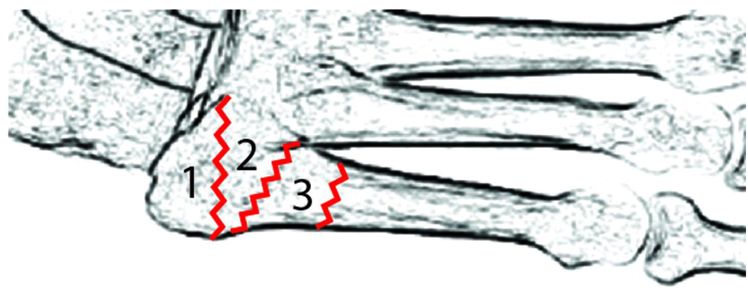
Illustration demonstrates the zonal anatomy at the base of the fifth metatarsal. Zone 1 fracture (most proximal) is an avulsion type. Zone 2 fracture (Jones fracture) occurs at the metaphyseal–diaphyseal junction. Zone 3 fracture is a proximal diaphyseal fracture.
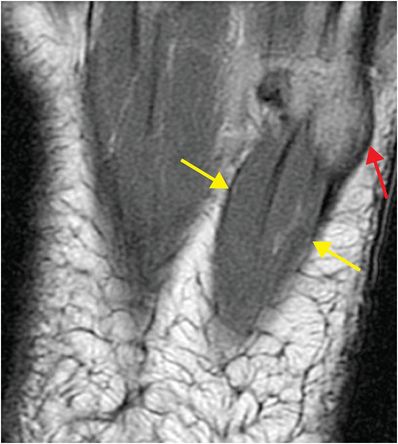
Axial PD-weighted MR of the base of the fifth metatarsal demonstrates normal anatomy of the lateral cord of the plantar aponeurosis (yellow arrows) inserting onto the base of the fifth metatarsal (red arrow)
Imaging of fifth metatarsal fractures
Radiographs are the primary modality for imaging proximal fifth metatarsal fractures.
Once the fracture has been identified on radiographs, attempts should be made to describe the zonal location, etiology (acute or stress fracture), degree of displacement, and the presence of intra-articular extension.
Treatment of fifth metatarsal fractures
As a general principle, indications for surgical treatment include a more distal fracture, displacement of more than 2 mm, and intra-articular extension. Competitive athletes may also be treated surgically without these indications. Otherwise, most fractures are treated conservatively.
The junction of the metatarsal metaphysis and diaphysis has a watershed vascular supply. With repetitive mechanical forces from weight-bearing, fractures in this tenuously vascularized region are susceptible to delayed healing.
Clinical synopsis
This patient, a 47-year-old female with a zone 2 acute fifth metatarsal fracture, was sent home from the Emergency Department with compression bandaging and crutches. A week later she was seen in the orthopedic clinic and underwent elective intramedullary screw fixation of the fifth metatarsal.
Self-assessment
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree