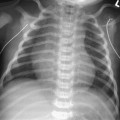
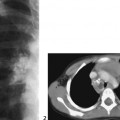
CASE 88 A 3-year-old female presents with leg-length discrepancy (LLD). Figure 88A A frontal view of the pelvis demonstrates shortening with proximal deformity of the left femur (Fig. 88A). A small, left femoral head epiphyseal ossification center is present within a dysplastic acetabulum, and this epiphysis shows no bony continuity with the superolaterally displaced femoral shaft. The proximal end of the ossified femoral shaft is irregular with bone inhomogeneity and sclerosis. Proximal focal femoral deficiency (PFFD) PFFD, also known as longitudinal deficiency of the femur, is defined as a deficiency of iliofemoral articulation associated with limb malrotation and leg-length discrepancy (LLD). This rare anomaly (incidence 1 in 52,000) presents as a spectrum of defects ranging from mild femoral hypoplasia with varus bowing to complete absence of the proximal femur and acetabulum. Most observers consider PFFD as a sporadic condition; however, several hereditary case reports have been reported. Associated anomalies are seen in —65% of patients, the most common being ipsilateral fibular hemimelia, which is seen in 50%. Numerous hip, knee, ankle, and foot anomalies have been described, including abnormalities of the contralateral extremity in 25% and bilateral involvement in 15%. Given the wide spectrum of deformities, it is unlikely that there is a single etiologic factor producing PFFD. A developmental insult between 4 and 6 weeks’ gestation is suspected with anoxia, ischemia, trauma, infection, irradiation, or thermal injury all proposed as possible agents. Thalidomide is the only agent proven to cause PFFD. Patients have a characteristic appearance with the hip flexed, abducted, and externally rotated. The thigh is short and bulky and tapers to the knee resulting in a shape described as a “ship’s funnel.” Most patients can walk; however, they have an abnormal gait (abductor lurch).
Clinical Presentation
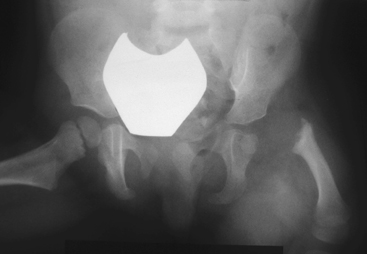
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Etiology
Clinical Findings
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree