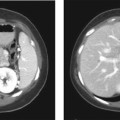
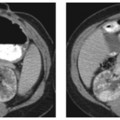
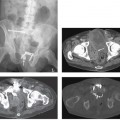
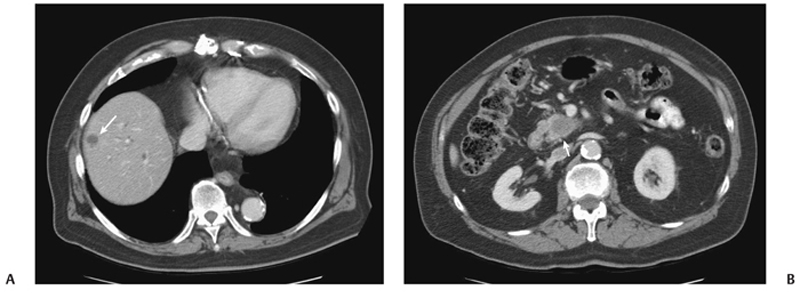
CASE 9 A 71-year-old man presents with abdominal pain, anorexia, and weight loss over the last few months. Fig. 9.1 (A) An axial contrast-enhanced CT scan shows a small hypoattenuating lesion in the right lobe of the liver (arrow). There is biliary ductal dilatation. (B) Axial image at a lower level shows a hypodense primary pancreatic neoplasm (arrow). An axial contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scan (Fig. 9.1) shows a small hypoattenuating lesion in the right lobe of the liver. There is biliary ductal dilatation accompanied by a hypodense mass in the pancreatic head. Liver metastasis from primary pancreatic cancer The liver represents the most common organ affected by metastatic disease. Gastrointestinal (GI) malignancies, especially colorectal carcinoma, and other primary tumors (more often breast, lung, and pancreas carcinoma and melanoma) can easily spread to the liver parenchyma. Liver metastases are usually not clinically significant. Prominent multiple metastases can cause obstruction of the biliary system and therefore jaundice. Hemoperitoneum caused by spontaneous rupture of hepatic metastases is uncommon but has been reported in patients with lung carcinoma, renal cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Clinical Findings
Complications
Etiology
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree