Case 90
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
A 68-year-old man with difficulty urinating.
 Imaging Findings
Imaging Findings
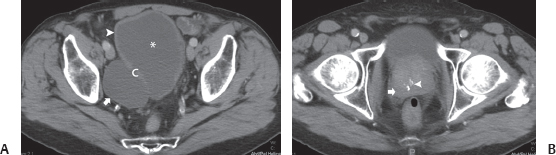
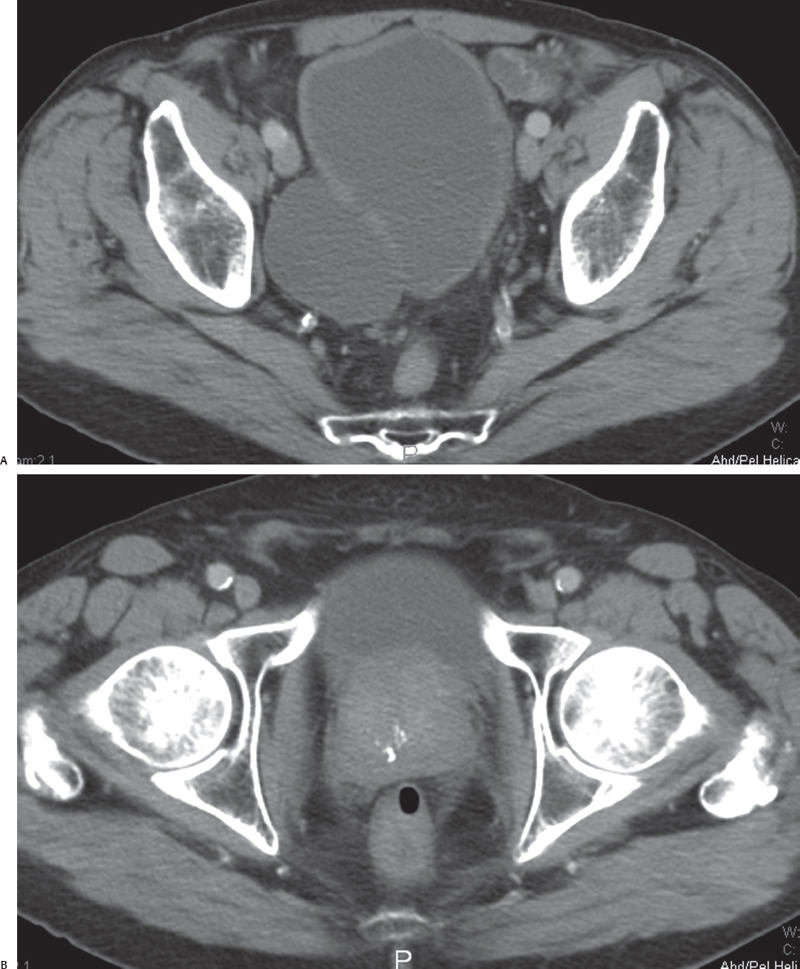
(A) Postcontrast axial computed tomography (CT) image obtained at the level of the urinary bladder shows a fluid-filled structure (arrow) adjacent to the urinary bladder (asterisk). There is a subtle communication (C) between the larger abnormality and the urinary bladder. The wall of the urinary bladder (arrowhead) is thickened. No filling defect is seen. (B) Postcontrast axial CT image obtained at a level below that of Figure B shows that the prostate is enlarged (arrow). Calcifications (arrowhead) are seen within the prostate.
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
• Acquired bladder diverticula due to bladder outlet obstruction by an enlarged prostate: These outpouchings of the urinary bladder mucosa are usually due to an underlying bladder outlet obstruction or neurogenic problems of bladder emptying. Their location is random and not related to the ureteric orifices. Their walls are characteristically thin.
• Hutch diverticula:
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


