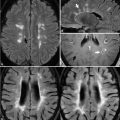
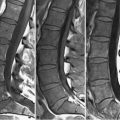
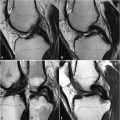
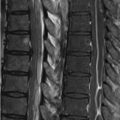
98 Adverse Reactions Despite marketing strategies implying the contrary, no rigorous study has ever demonstrated a difference in the frequency of mild adverse reactions—which include nausea (1.5%) and urticaria (0.5%)—among the various gadolinium chelate contrast agents. Severe anaphylactoid reactions with such agents are rare and even more rarely result in death. Treatment is similar to that for reactions induced by iodinated contrast media, initially consisting of cessation of agent injection and inhaled oxygen. Urticaria alone may only require use of diphenhydramine for treatment, whereas laryngeal edema and/or bronchospasm require administration of intramuscular epinephrine (1:1,000), supplemented for bronchospasm by an inhaled bronchodilator. The treatment of hypotension (alone or with tachycardia) is fluid resuscitation. Hypotension with bradycardia (vagal reaction) may require IV atropine as well. Gadolinium chelates do cross the placenta and persist in amniotic fluid. The effects of this are unknown, although no teratogenic consequences have been observed to date in humans. Gadolinium chelates should only be administered in pregnancy if the desired information can be obtained by no other means and if such information is crucial to the fetus or patient imminently during pregnancy. In this case, macro-cyclic agents should be administered at the smallest dose possible. Breast feeding should be avoided within 24 hours of gadolinium chelate administration. Gadolinium chelates are not nephrotoxic. However, in patients with renal failure (glomerular filtration rate [GFR] <30 mL/min per 1.73 m2
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree