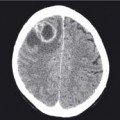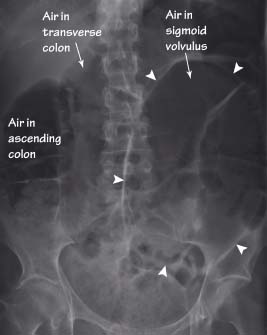
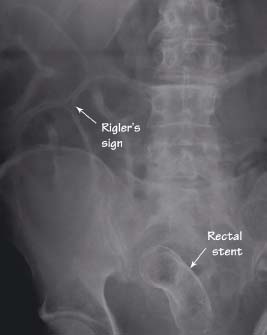
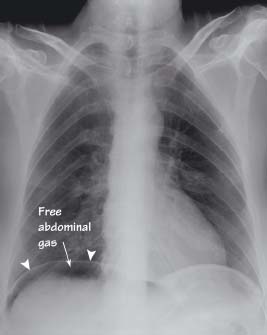
Bowel obstruction
Obstruction of the bowel may be complete or incomplete, acute or chronic, and mechanical or non-mechanical (ileus). The causes include extramural (e.g. adhesions, herniae, volvulus and tumour), intramural (e.g. Crohn’s disease, tumours and strictures), and intraluminal pathology (e.g. faecal impaction, gallstone ileus and foreign bodies).
Bowel obstruction can be divided into two types, small and large bowel obstruction, due to the different locations and AXR appearances. The obstructing lesion is often not seen on the AXR but it is important to remember that the bowel proximal to it distends and the bowel distal collapses. The collapsed bowel will therefore not appear on the AXR but identifying this zone of transition will help locate the site of the obstruction. Distal obstructions consequently cause large bowel distension and if there is an incompetent ileocaecal valve, leakage of gas from the large into the small bowel, results in large and small bowel distension on the AXR.
Small bowel obstruction (SBO)
The commonest cause of small bowel obstruction is postoperative adhesions
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree