Start |
Standing |
|
Give: gas pills, water; fluoro for position; drink 2-3 gulps thick barium (hold cup in L hand near L shoulder) |
Spot filming—thick barium |
Stand |
LPO |
– 2/1 air esophagram (include gastroesophageal junction [GEJ]), two exposures |
Coat |
|
– Finish at least 3/4 of barium, face table, bring table down with patient prone, then position L lateral, then supine. |
Supine |
AP |
– 1/1 body stomach (in air) |
|
LPO |
– 1/1 antrum stomach (in air); try air bulbb |
|
RPO |
– 1/1 Schatzki view and body stomach (include lesser curve) |
R lateral |
|
– 1/1 anterior wall and GEJ (in air) and duodenal bulb |
Prone |
PA |
– 1/1 body and antrum stomach (over bolster) |
|
RAO |
– 2/1 antrum, bulb and C-sweep (with compression) |
[L lateral]b |
Spot filming—thin barium |
Prone |
RAO |
Fluoro: observe single big swallow of thin barium from thoracic inlet to GEJ; observe stripping wave |
|
|
2/1 drinking esophagram [over bolster] (include GEJ), two exposures |
Supine |
AP |
Check for GE reflux, document level if present |
[Supine LPO]b |
Stand |
LPO |
1/1 fundus stomachb |
|
|
4/1 bulb, antrum (with compression), two exposures |
|
AP |
4/1 proximal and distal stomach (with compression), one to two exposures |
Finish up |
|
|
Overheads: routine |
aSpot film (9″ × 9″) formats: 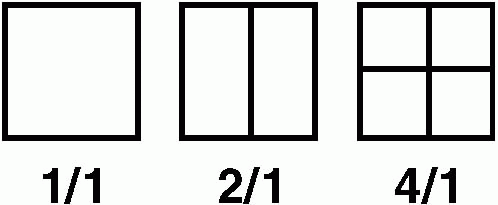 |
b 2/1 Opportunities to image the duodenal bulb in air (“air bulb”); make two exposures (include antrum and bulb, then bulb and C-sweep). (Trick: Try turning patient prone LAO to drain excess barium from the duodenal bulb and to fill it with air; then turn patient back to supine LPO for spot film.) |

