Bronchiolitis, Constrictive
Melissa L. Rosado-de-Christenson, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Terminology
Concentric peribronchiolar fibrosis of membranous and respiratory bronchioles
Imaging Findings
Radiography
Normal chest radiographs
Hyperinflation
CT/HRCT
Mosaic pulmonary attenuation
Air-trapping on expiratory CT/HRCT
Low attenuation; air-trapping and reflex vasoconstriction
High attenuation; redistribution of blood flow to relatively normal lung
Bronchial dilatation, bronchiectasis, bronchial wall thickening
Top Differential Diagnoses
Panlobular Emphysema
Pulmonary Hypertension
Asthma
Pathology
Etiologies
Postinfectious
Post-transplantation
Collagen vascular disease
Inhalational injury
Nonuniform bronchiolocentric fibrosis
Clinical Issues
Progressive dyspnea, cough
Diagnostic Checklist
Expiratory HRCT for detection of air-trapping
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations and Synonyms
Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS)
Definitions
Bronchiolitis = broad spectrum of inflammatory and fibrotic changes centered on small conducting airways
Confusing and often inconsistent terminology
Bronchiolitis obliterans refers to both constrictive bronchiolitis and bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia
Obliterative bronchiolitis refers to clinical syndrome of airflow obstruction associated with HRCT findings of air-trapping
Various classification schemes
Classification based on etiology and clinical syndromes
Classification based on histologic features
Constrictive bronchiolitis = peribronchiolar fibrosis with resultant bronchiolar narrowing or obstruction
No fibroblastic proliferation
Collagen deposition extrinsic to airway lumen
Diffuse patchy involvement
Irreversible process
Swyer-James-MacLeod syndrome = unilateral or focal postinfectious constrictive bronchiolitis
BOS = post-transplantation airflow obstruction
Clinical diagnosis; decrease in FEV1 from baseline
Potential BOS (BOS 0-p) = decrease in forced expiratory flow in mid expiratory phase &/or milder decrease in FEV1
Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia or cryptogenic organizing pneumonia
Cellular bronchiolitis with fibroblastic proliferation
Process confined to airway lumen
Often localized
Resolution with treatment
IMAGING FINDINGS
General Features
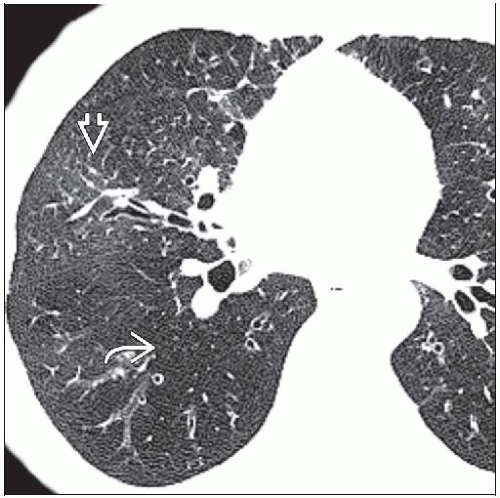
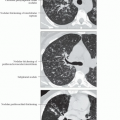
Best diagnostic clue: Lobular mosaic attenuation accentuated by expiratory imaging
CT Findings
Minimum intensity projection (MinIP)
Projects lowest attenuation voxels on every view through volume onto 2D image
Optimal visualization of diffuse lung disease, airways, and ground-glass opacity
Maximum intensity projection (MIP)
Projects highest attenuation voxels on every view throughout volume onto 2D image
Optimal visualization of nodules and vessels
Mosaic attenuation on inspiratory CT/HRCT
Heterogeneous lung attenuation
Alternating ↓ and ↑ lung attenuation
Reflects nonuniform bronchiolar obliteration
Hyperlucent underventilated (air-trapping) and underperfused lung (hypoxic vasoconstriction)
Normal or near normal inspiratory CT/HRCT
Mosaic attenuation may only be visible on expiratory imaging
Diffuse decreased lung attenuation in severe disease
May be subtle
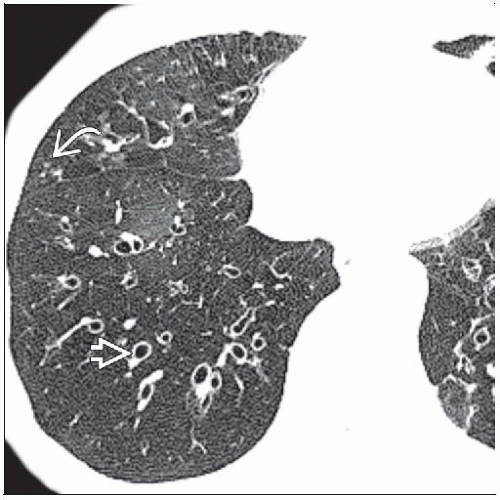
Air-trapping on expiratory HRCT
Geographic areas of decreased lung attenuation
Decreased vessel caliber from hypoxic vasoconstriction
No decrease in volume of affected lung
Areas of increased (normal) lung attenuation
Increased vessel caliber and blood flow
Decrease in volume
Well- or poorly defined margins
May be seen in patients without any disease
Typically smokers and elderly individuals
Frequent in lower lobe superior segments and inferior lingula
Involves < 25% of CT cross-sectional area
Lobular air-trapping of < 3 adjacent secondary lobules in 50% of asymptomatic patients
Associated findings
Proximal bronchial dilatation, bronchiectasis, bronchial wall thickening
Common in post-transplantation and postinfectious constrictive bronchiolitis
Scant centrilobular nodules
Pulmonary nodules & mosaic attenuation
Consider diffuse idiopathic neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia
Predisposed to pneumothoraces, pneumomediastinum
Swyer-James-MacLeod syndrome
Focal lung hyperlucency and decreased vascularity
Normal or decreased volume of affected lung
Air-trapping in affected lung on expiratory CT/HRCT
Areas of decreased attenuation and air-trapping of other lobes or contralateral lung
Radiographic Findings
Radiography
Normal chest radiograph
Nonspecific findings
Hyperinflation
Peripheral attenuation of vascular markings
Swyer-James-MacLeod syndrome
Unilateral hyperlucent lung
Decreased pulmonary vascularity
Normal or decreased volume of affected lung
Small ipsilateral hilum
Air-trapping on expiratory radiography
MR Findings
Hyperpolarized 3-helium MR imaging; more sensitive than HRCT for detection of air-trapping
Imaging Recommendations