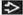Broncholithiasis
Jud W. Gurney, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Terminology
Calcified or ossified material within bronchial lumen, usually due to erosion from adjacent lymph nodes
Imaging Findings
Endobronchial or peribronchial calcified nodule at CT associated with signs of bronchial obstruction
Most common right middle lobe and anterior segmental bronchi upper lobes
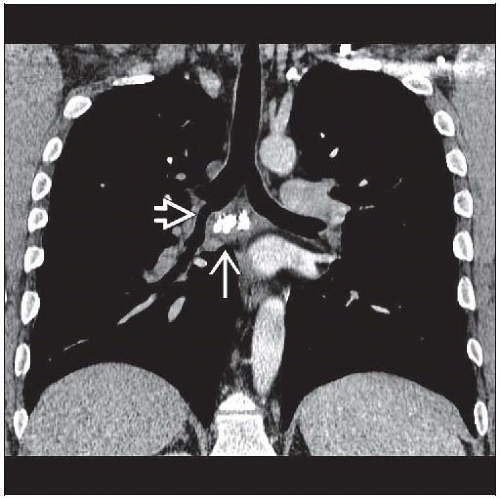
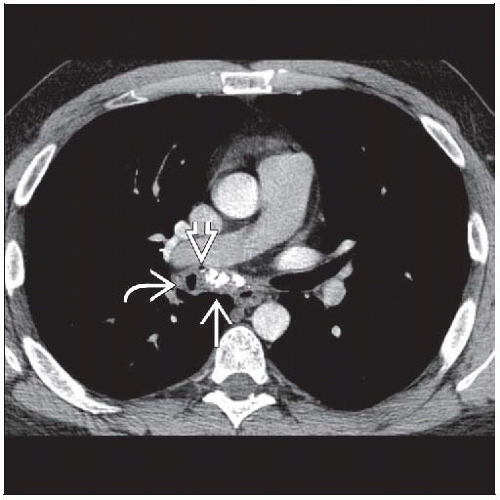
Broncholith
Distorts adjacent airway, which is narrowed but remains patent (50%) or
Calcified lymph nodes completely obstructs lumen (50%)
Majority of lymph node calcified, soft tissue component < 10%
Usually solitary, rarely multiple
Extraluminal air nearly diagnostic of erosion into bronchus
Top Differential Diagnoses
Aspiration
Carcinoid
Mediastinal Fibrosis
Silicosis
Pathology
Vary in size, 2-15 mm in diameter
Irregular shape with sharp angles
Clinical Issues
Lithoptysis: Expectoration of calcified material (15%)
Bronchoscopy: Calcified material usually not evident (50%), obscured by inflammatory tissue
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Calcified or ossified material within bronchial lumen, usually due to erosion from adjacent lymph nodes
Includes aspiration of bone or calcified material, erosion of calcified cartilage into airway, migration of calcified material from distant site such as pleural plaque or gallstone
IMAGING FINDINGS
General Features
Best diagnostic clue: Endobronchial or peribronchial calcified nodule at CT associated with signs of bronchial obstruction
Patient position/location
Most common right middle lobe and anterior segmental bronchi upper lobes
Right-sided > left-sided (2:1)
Size: 2-15 mm
Morphology
Irregular shape and angular
Majority of lymph node calcified, soft tissue minimal
CT Findings
Broncholith
Peribronchial lymph node either
Distorts adjacent airway, which is narrowed but remains patent (50%) or
Calcified lymph nodes completely obstructs lumen (50%)
Majority of lymph node calcified, soft tissue component (< 10%)
Extraluminal air nearly diagnostic of erosion into bronchus
Usually solitary, rarely multiple
Does not enhance with intravenous contrast
Signs of bronchial obstruction
Atelectasis (66%)
Postobstructive pneumonia (33%)
Bronchiectasis (33%)
Air-trapping (5%)
Location
Radiographic Findings
Radiography
Usually nonspecific and rarely diagnosed
Signs of bronchial obstruction
Lobar to subsegmental atelectasis
Postobstructive pneumonia
Mucoid impaction
Bronchiectasis
Air-trapping (rare)
Signs of granulomatous disease common
Calcified lung nodules + calcified hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes (Ranke complex)
Broncholith
Calcified nodule in airway rarely evident
Gradual decrease in size of calcified hilar or mediastinal lymph nodes or
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree