and Jurgen J. Fütterer2, 3
(1)
Department of Radiological Sciences, Oncology and Pathology, Sapienza University of Rome, Rome, Italy
(2)
Department of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, Radboudumc, Nijmegen, The Netherlands
(3)
MIRA Institute for Biomedical Technology and Technical Medicine, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands
Claustrophobia
20 % of general population have claustrophobia.
Patient positioning important: Try prone position or head outside the bore or gantry.
Mild sedation (e.g., benzodiazepine) can be applied.
Cervical Carcinoma
Cervical epithelium can undergo a series of gradual histologic changes from progressively severe dysplasia to carcinoma in situ (CIS) and invasive carcinoma.
Invasive carcinoma spreads by direct extension to adjacent organs: vagina, pelvic wall, bladder, and rectum. Metastatic lymphadenopathy occurs commonly in the pelvic lymph nodes, but it also involves the periaortic chains in about 20 % of patients.
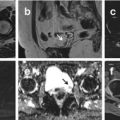
The identification of cervical carcinoma in MRI is simple because the high-signal-intensity lesion contrasts with the marked low-signal-intensity cervical stroma on T2W images. Areas of coagulative necrosis may appear as small foci of lower signal intensity within the tumor mass.
Tumors responding to treatment generally lose signal intensity on T2W images.
T1W images often doesn’t detect smaller lesions because of a lack of contrast between the cervix and tumor.
Cryptorchidism
The prevalence of undescended testis is 3.5 % at birth and decreases to 0.8 % by 1 year, because many testes descended spontaneously.
Identification of undescended testis is important because of the increased incidence of infertility and neoplasm if the testis remains undescended.
If US findings are equivocal or negative and/or a preoperative localization is desired, either CT or MRI can be performed.
MRI is the best cross-sectional modality to assess cryptorchidism. A disadvantage of MRI in children, compared with CT, is the lack of a contrast agent to opacify bowel loops, which makes detection of the atrophic testis more difficult. Young children require sedation which may be a limiting factor for MR imaging.
The CT features of an undescended testis are an oval and soft tissue mass located anywhere along the pathway of testicular descent. The accuracy of CT for localization of non-palpable testes exceeds 90 %. Unless it is atrophic or ischemic, the undescended testis has an intermediate signal intensity equal to that of muscle on T1-weighted images and higher than that of subcutaneous fat on T2-weighted images. Coronal T1W images can show gubernaculum testes and spermatic cord, which can be followed to locate the undescended testes. Diffusion-weighted MRI shows markedly hyperintense testes and helps to differentiate it from surrounding structures.
Cystectomy
Cystectomy is the surgical removal of the urinary bladder; it is most commonly performed for bladder cancer treatment. After the bladder has been removed, an ileal conduit urinary diversion is necessary. An alternative is to construct a pouch from a section of the ileum or colon, which can act as a form of replacement bladder.
Because of the complexity of these procedures, early and late postsurgical complications are frequent (including hematoma, urinoma, and abscess); CT is an accurate method for detecting these complications.
Afterwards, a cutaneous ureterostomy CT allows the accurate depiction of ureters and their surgical anastomoses to the anterior abdominal wall.
After, an ileal conduit creation multidetector CT allows visualization of the ureters up to the point of anastomosis to the ileal conduit. It is important to evaluate also the enteroenteric anastomosis, most often visible because mechanical suturing is usually performed.
Subsequently, in continent cutaneous diversion at multidetector CT, the reservoir appears to be partially filled by hypoattenuating material, a characteristic that represents mucous secretions from the bowel.
Subsequently, an orthotopic bladder replacement multidetector CT allows the identification of a bowel loop in anatomic continuity with the reservoir, a finding that corresponds to the isoperistaltic afferent limb.
Early complications:
Adynamic ileus is the most common bowel complication after urinary diversion surgery: it is characterized by dilated loops of small and large bowel with gas–fluid levels and by the absence of a visible cause of obstruction. A CT-based diagnosis of adhesive small bowel obstruction may be made in the presence of an abrupt change in bowel caliber and the absence of another cause of obstruction.
Fluid collection: The differential diagnosis of postsurgical fluid collections includes urinoma (see section “Urinoma”), hematoma, and lymphocele. Unenhanced and nephrographic phase in the presence of hematoma shows a non-enhancing heterogeneous fluid collection. The CT finding of a homogeneous fluid collection with a very thin wall near the surgical clips is suggestive of lymphocele.
Contrast-Induced Nephropathy
Contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) is defined as the impairment of renal function; it is measured as either a 25 % increase in serum creatinine (SCr) from baseline or 0.5 mg/dL (44 μmol/L) increase in absolute value, within 48–72 h of intravenous contrast administration. Following contrast exposure, SCr levels peak between 2 and 5 days and usually return to normal in 14 days.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree