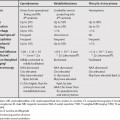
72 Calcification in hepatic lesions is nonspecific and can be seen in a wide range of infectious lesions and primary and metastatic tumors. In certain cases, the presence of calcification is helpful in narrowing the differential diagnosis. For example, in a liver lesion with a central scar, the presence of calcification suggests fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma rather than focal nodular hyperplasia. Fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma has a reported incidence of calcification as high as 68%.1 The calcification(s) are usually small and located centrally in the fibrous scar. Calcification in hemangiomas can appear as multiple spotty calcifications (phleboliths) or large, usually central, areas of calcification.2 Calcification can be seen secondary to mucous secretions. Calcification is more common in cholangiocarcinoma than in untreated hepatocellular carcinoma.3 Calcifications are often located eccentrically, and may be seen in cystic areas related to hemorrhage or necrosis.2,4
Calcified Liver Lesions
Features of Specific Tumors with Calcification
Fibrolamellar Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hemangioma
Cholangiocarcinoma
Hepatocellular Adenoma
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree